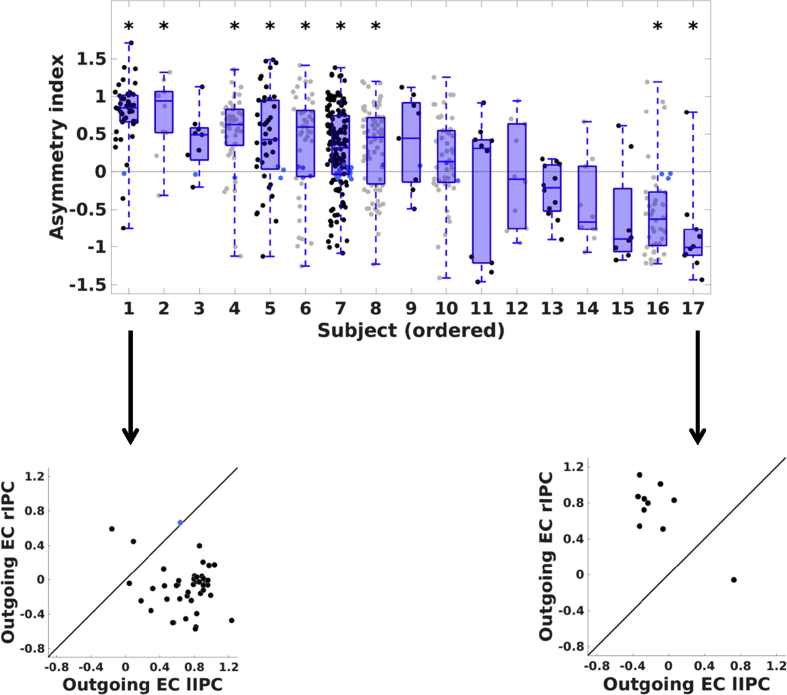
Fig. 4.
Upper panel: Session-specific hemispheric asymmetry for all subjects, in order of decreasing proportion of left hemisphere-dominant sessions. The asymmetry index was computed as the average efferent influence from the left minus the mean efferent influence from the right IPC. Dots represent the asymmetry index for each session of the respective subject (positive = left dominant; negative = right dominant). Blue dots depict sessions without evidence for hemispheric dominance. Asterisks above data clouds indicate subjects with stability in asymmetry significantly different from zero (FDR = 5%). Blue box plots of subject-specific asymmetry indices are superimposed on data clouds. Lower panels: Hemispheric asymmetry for the most stable left and right asymmetric subject. Black circles represent the average outgoing influence from left (x-axis) and right IPC (y-axis). Circles below the reference line indicate sessions with higher influence from left IPC, circles above the reference line depict sessions with higher influence from right IPC. Light-blue circles depict sessions for which asymmetry did not survive the posterior probability criterion.