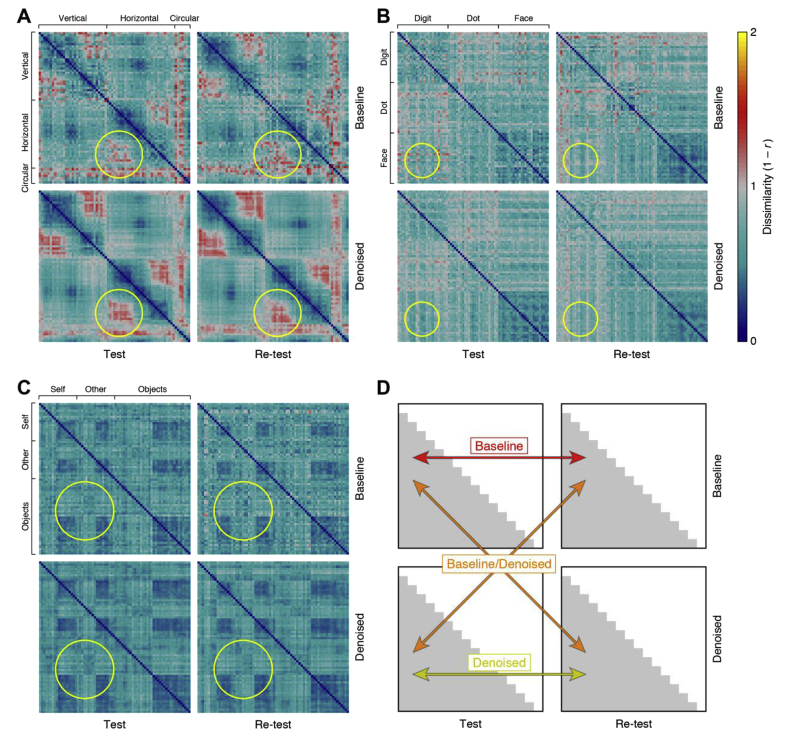
Fig. 1.
GLMdenoise improves the quality of representational dissimilarity matrices (RDMs).
Each participant's fMRI dataset was split into two halves (Test, Re-test), and each half was analyzed with a standard GLM (Baseline) or with GLMdenoise (Denoised). The results of each analysis are used to construct an RDM, which indicates the dissimilarity between the multivoxel activity patterns associated with each pair of experimental conditions. (A) Results for a participant from Experiment 1 (Participant 3). The yellow circle highlights a section of the RDMs for which denoising yields clearer structure and improves replicability across splits of the data. (B) Results for a participant from Experiment 2 (Participant 4). Same format as A. (C) Results for a participant from Experiment 4 (Participant 26). Same format as A. (D) Metrics of RDM quality. We computed three metrics quantifying the replicability of the lower triangles of the RDMs. Baseline is the test-retest correlation of the undenoised RDMs. Denoised is the test-retest correlation of the denoised RDMs. Baseline/Denoised is the correlation between an undenoised RDM and a denoised RDM (correlation values for the two possible cases are averaged). See Supplementary Fig. 1 for RDM results for all participants.