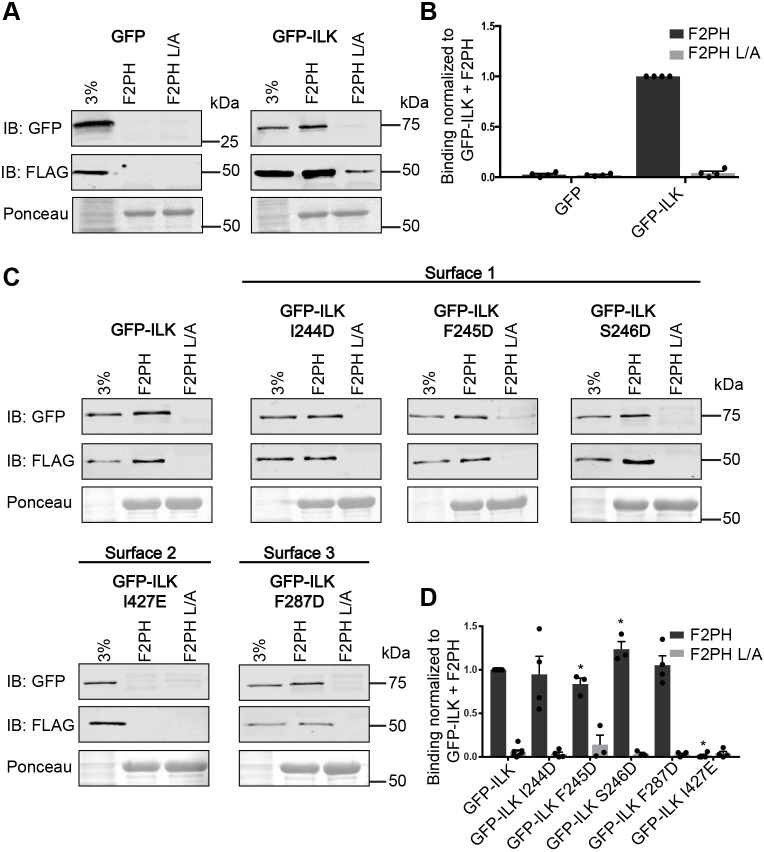
Fig. 2.
I427E mutation of αH in surface 2 of ILK-pKD impairs binding of GFP–ILK to GST–kindlin-2 F2PH. (A) GFP or GFP–ILK co-expressed with FLAG–α-parvin in CHO cells bound to glutathione bead-immobilized GST–kindlin-2 F2PH or GST–kindlin-2 F2PH L357A (L/A) as a negative control detected by immunoblotting. One representative blot for each construct tested is shown. The lane labeled ‘3%’ indicates 3% of input lysate. Bead loading was visualized by Ponceau S staining. (B) Quantification of GFP or GFP–ILK binding to GST–kindlin-2 F2PH or GST–kindlin-2 F2PH L/A (mean±s.e.m.; n=4). (C) Representative immunoblots for pulldown of GFP–ILK mutants co-expressed with FLAG–α-parvin in CHO cell lysates by GST–kindlin-2 F2PH or GST–kindlin-2 F2PH L/A. The lane labeled ‘3%’ indicates 3% of input lysate. Bead loading was visualized by Ponceau S staining. (D) Quantification of binding of GFP–ILK and GFP–ILK mutants to GST–kindlin-2 F2PH or GST–kindlin-2 F2PH L/A (mean±s.e.m.; n≥3); *P<0.005 (Student's t-test). Pulldown quantification graphs are shown as bar charts with individual data points plotted (dots).