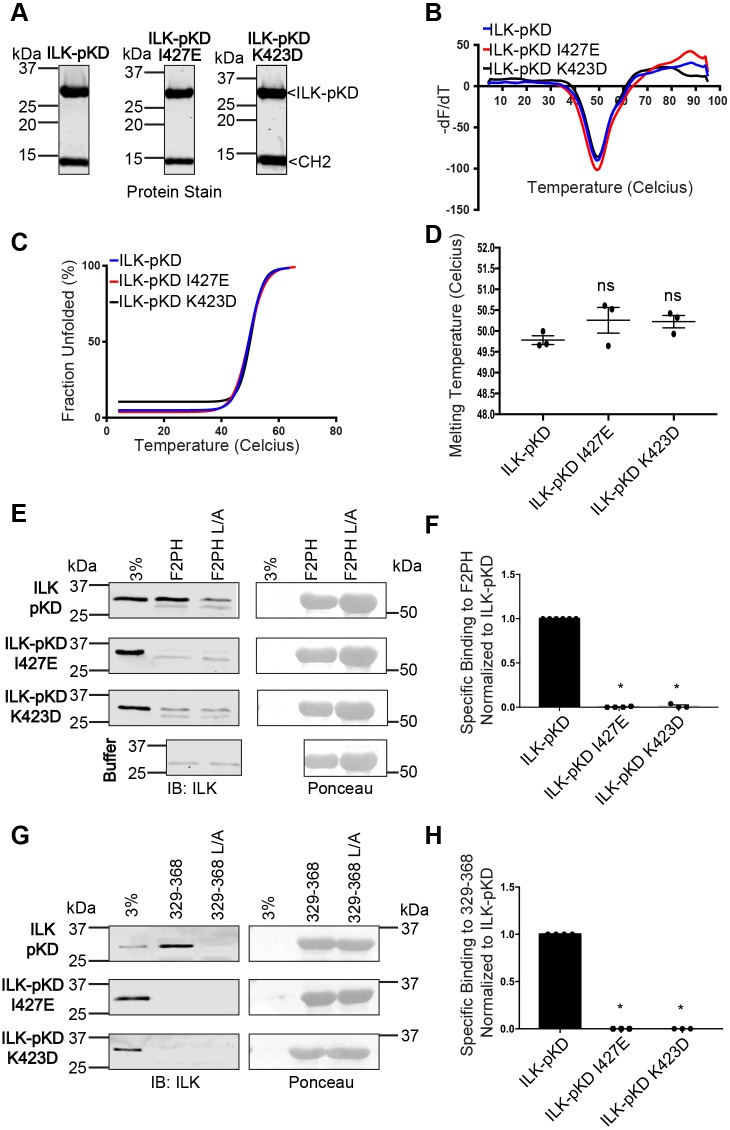
Fig. 4.
ILK-pKD mutants that are defective in binding kindlin-2 co-purify with α-parvin-CH2 and are structurally stable. (A) Coomassie protein stain of purified non-mutant ILK-pKD, ILK-pKD I427E and K423D ILK-pKD–α-parvin-CH2 complexes. (B) Negative derivatives of SYPRO Orange fluorescence with respect to temperature for the non-mutant ILK-pKD, ILK-pKD I427E and K423D ILK-pKD–α-parvin-CH2 complexes from one representative experiment. (C) Normalized SYRPO Orange fluorescence data fitted to a Boltzmann sigmoid by using Graphpad Prism software for the purified ILK-pKD–α-parvin-CH2 complexes from one representative experiment. Statistical fit parameters: non-mutant ILK-pKD: r2=0.99, V50=49.7±0.2 (V50±s.e.m.); ILK-pKD I427E: r2=0.99, V50=49.7±0.2; ILK-pKD K423D: r2=0.95, V50=50.4±0.4. (D) Melting temperature extracted from the half-maximal point of the fitted fluorescence data (mean±s.e.m.; n=3); ns, not significant, P>0.05 (Student's t-test). (E,F) Pulldown of purified ILK-pKD–α-parvin-CH2 complexes by immobilized GST–kindlin-2 F2PH or GST–kindlin-2 F2PH L357A (L/A) assessed by representative immunoblots (E) and quantified (F) (mean±s.e.m.; n≥3); *P≤0.0001 (Student's t-test). (G,H) Pulldown of purified ILK-pKD–α-parvin-CH2 complexes by immobilized GST–kindlin-2 329-368 or GST–kindlin-2 329-368 L/A assessed by representative immunoblots (G) and quantified (H); mean±s.e.m.; n≥3; P≤0.0001 (Student's t-test). Pulldown quantification is shown as bar charts with individual data points plotted (dots). GST-protein loading for pulldowns is indicated by Ponceau S staining.