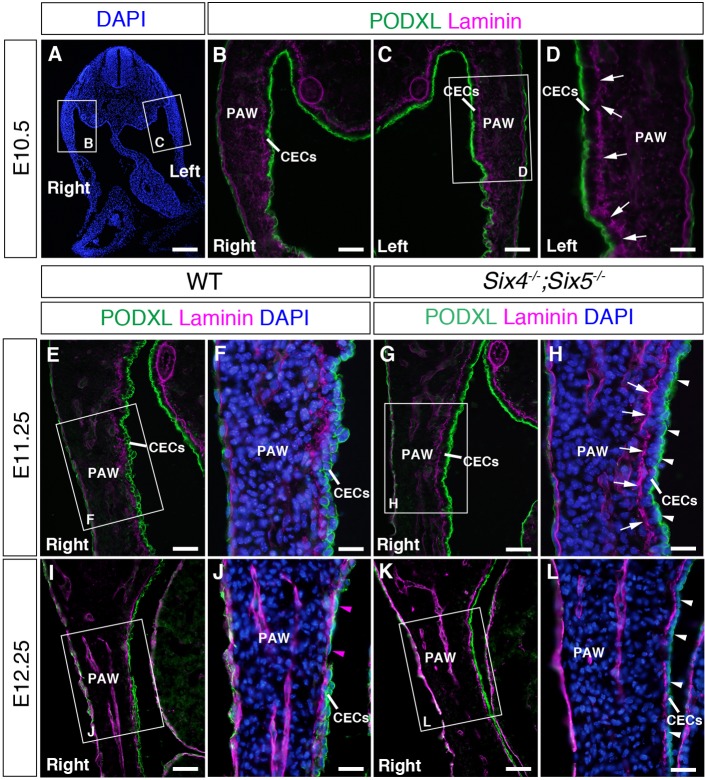
Fig. 6.
Transition of CECs to mesothelial progenitor cells in wild-type embryos and impaired mesothelium formation in Six4−/−;Six5−/− embryos. (A-D) Distribution of laminin and PODXL in wild-type embryos at E10.5. B, C and D are magnified images of the boxed regions in A and C. Laminin localizes at the border between the mesenchymal region and the CE in the right (B) and left side (C, arrows in D) of the PAW. Note that laminin accumulates with a fragmented pattern at the border between the mesenchymal region and the CE in the right (B) and left side (C, arrows in D) at E10.5. PODXL accumulates in the apical side of CECs in the right (B) and left side (C,D). (E-H) Distribution of laminin and PODXL in the PAW of wild-type (E,F) and Six4−/−;Six5−/− embryos at E11.25 (G,H). F and H are magnified images of the boxed regions in E and G, respectively. PODXL distributes at the cell periphery of CECs at E11.25 (E,F). In Six4−/−;Six5−/− embryos, PODXL localizes in the apical domain of CECs in the PAW (arrowheads in H) and laminin accumulates with a less fragmented pattern (arrows in H) in contrast to wild-type embryos (F). (I-L) Distribution of laminin and PODXL in the PAW of wild-type (I,J) and Six4−/−;Six5−/− (K,L) embryos at E12.25. J and L are magnified images of the boxed regions in I and K, respectively. Cells with PODXL at their periphery and cells with squamous shape (arrowheads in J) are observed in the CE of wild-type PAW (J). PODXL localizes in the apical domain of CECs in the PAW of Six4−/−;Six5−/− embryos (arrowheads in L). Scale bars: 200 μm in A; 50 μm in B,C,E,G,I,K; 25 μm in D,F,H,J,L.