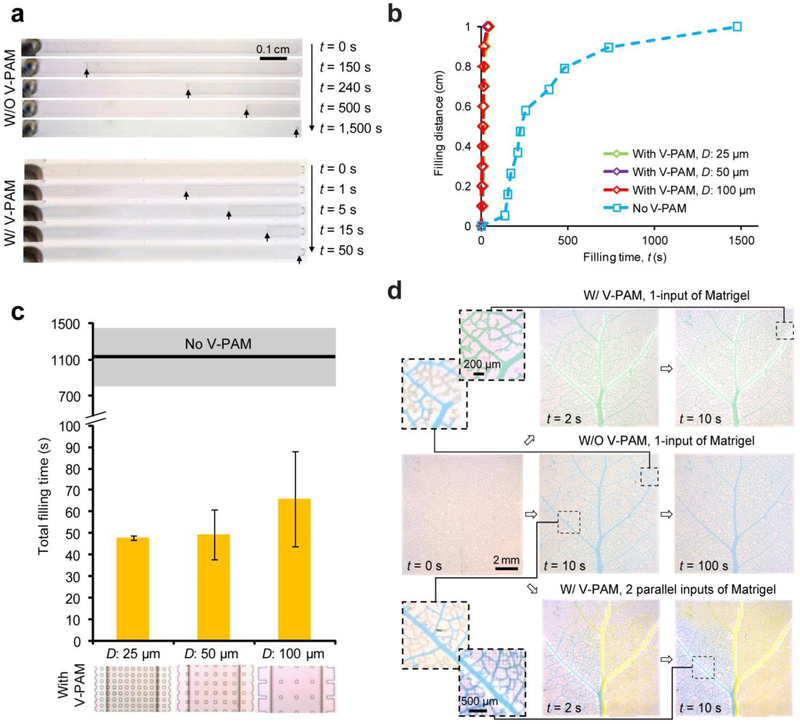
Figure 6.
Rapid filling of Matrigel solutions in microfluidic patterns with dead-end channels using V-PAM at room temperature (20 °C). (a) Bright field images showing filling of Matrigel solutions in straight, dead-end microchannels without (top) or with (bottom) V-PAM modules implemented. Images were recorded at different time points after the onset of the filling process (t = 0 s) as indicated. Arrows point to Matrigel solution fronts for easy visualization. For cases with V-PAM, W: 25 μm, D: 50 μm, and L: 1 cm. (b) Plot of Matrigel solution filling distance as a function of filling time t. (c) Comparison of total filling time between microchannels without or with V-PAM modules. V-PAMs with support pillar arrays of different separation distances D (D = 25, 50, 100 µm) were included. Mean (black line) ± S.D. (grey area) of total filling time for microchannels without V-PAM were included for comparison. (d) Bright field images showing leaf venation patterns filled with Matrigel solutions. 5% dyes were added to Matrigel for visualization. Paired zoom-in images were shown to compare filling of Matrigel solutions at the same leaf venation locations. Microvalves (not shown in images) below the main leaf branch were used to drive gel solutions through either 1 input or 2 parallel inputs. In all cases, S: 1.6 krpm, P: 12.5 psi, and V: 12.5 psi.