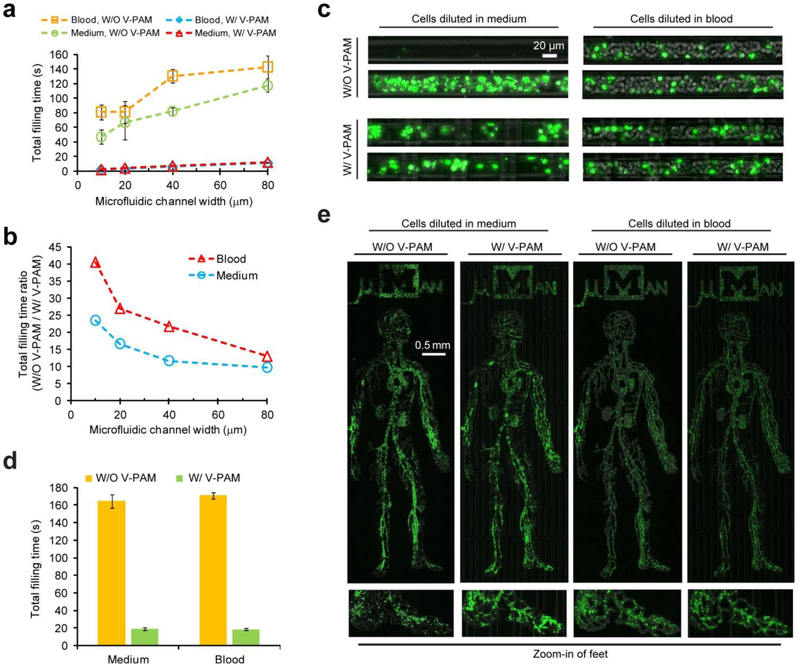
Figure 7.
Rapid filling of complex biofluids (cell suspensions or undiluted human whole blood) in microfluidic geometries with dead-end channels using V-PAM. (a) Plot of total filling time as a function of microfluidic channel width for filling cell suspensions in 0.5 cm-long, straight, dead-end microfluidic channels with a cross-section of 20 μm × 20 μm. For V-PAM, L: 0.5 cm. (b) Ratio of total filling times without V-PAM and with V-PAM plotted against microfluidic channel width. Data was extracted from (a). (c) Distribution of Hoechst-stained cells inside microfluidic channels after filling with cell suspensions. (d) Bar plot of total filling time for both cell suspensions and undiluted human whole blood to fill the µMan chip with or without V-PAM, as indicated. (e) Distribution of Hoechst-stained cells inside the µMan chip. Insets at the bottom show magnified views of the foot region. For all cases, microchannels were 20 μm thick, S: 1.6 krpm, P: 12.5 psi, and V: 12.5 psi.