Figure 2.
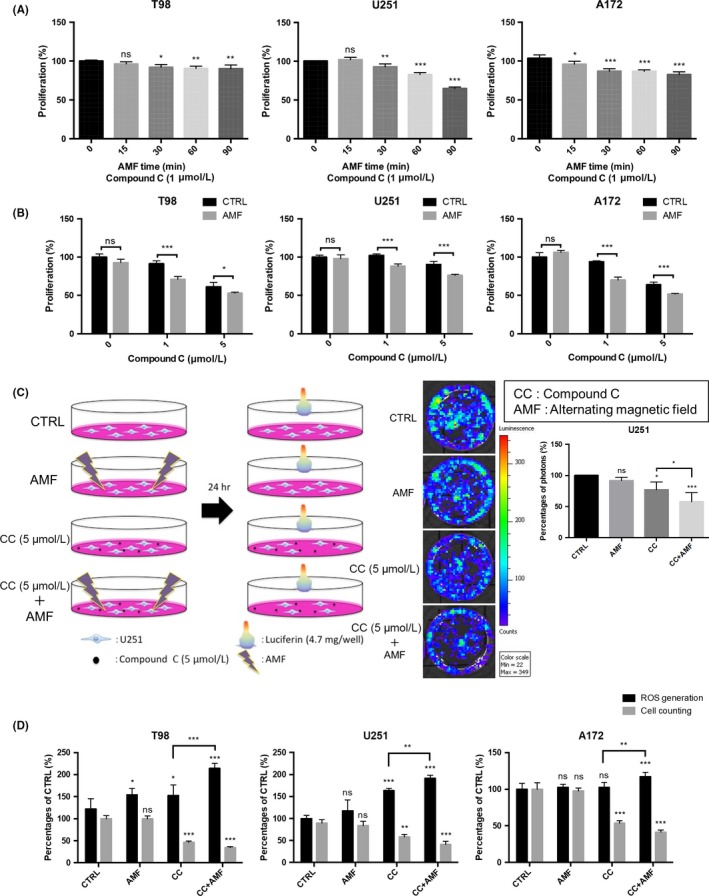
The alternating magnetic field (AMF) decreased the cell viability of glioblastoma (GB) cell lines in the presence of Compound C. A, Applications of the AMF for longer than 30 min increased the Compound C‐induced cytotoxicity in T98, U251, and A172 cells (n = 4; ns, not significant; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001). B, Compound C at 1 or 5 μmol/L exhibited cytotoxicity when combined with the AMF for 30 min in T98, U251 and A172 cells (n = 4; ns, not significant; *P < 0.05,**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). C, Viability analysis in the presence/absence of Compound C with/without the AMF for 30 min in U251 cells, which have been engineered to express the firefly luciferase gene. The viability of U251 cells was measured in terms of photon flux measured with an in vivo imaging system (IVIS). D, Quantification of cell viability with an IVIS imaging system. D, Effect of AMF for 30 min on ROS production in the absence/presence of Compound C (5 μmol/L) and the cell number counts for T98, U251 and A172 cells using the trypan blue assay (n = 4; ns, not significant; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001)
