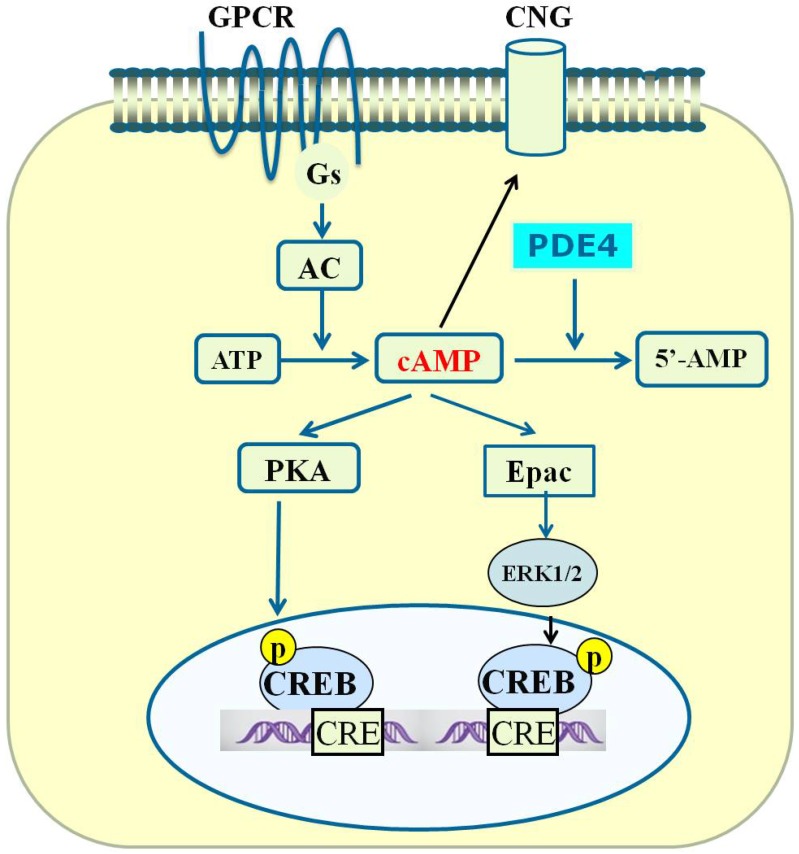
Fig 2.
PDE4-cAMP-mediated signaling pathways in neuronal cells. Activation of GPCR activates Gsα subunit and adenylyl cyclase (AC), which subsequently catalyzes the conversion of ATP to cAMP. Increase in the level of local intracellular cAMP leads to activation of protein kinase A (PKA), exchange proteins activated by cAMP (Epac) and cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG). Activated PKA phosphorylates a number of other proteins including cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB). Phosphorylated CREB binds to the cAMP-responsive element (CRE) and thereby modulates gene transcription. Activated Epac promotes the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2). Inhibition of PDE4 triggers an increase in cAMP which in turn exerts its downstream effects via activation of PKA/CREB and Epac/ERK signaling pathways.