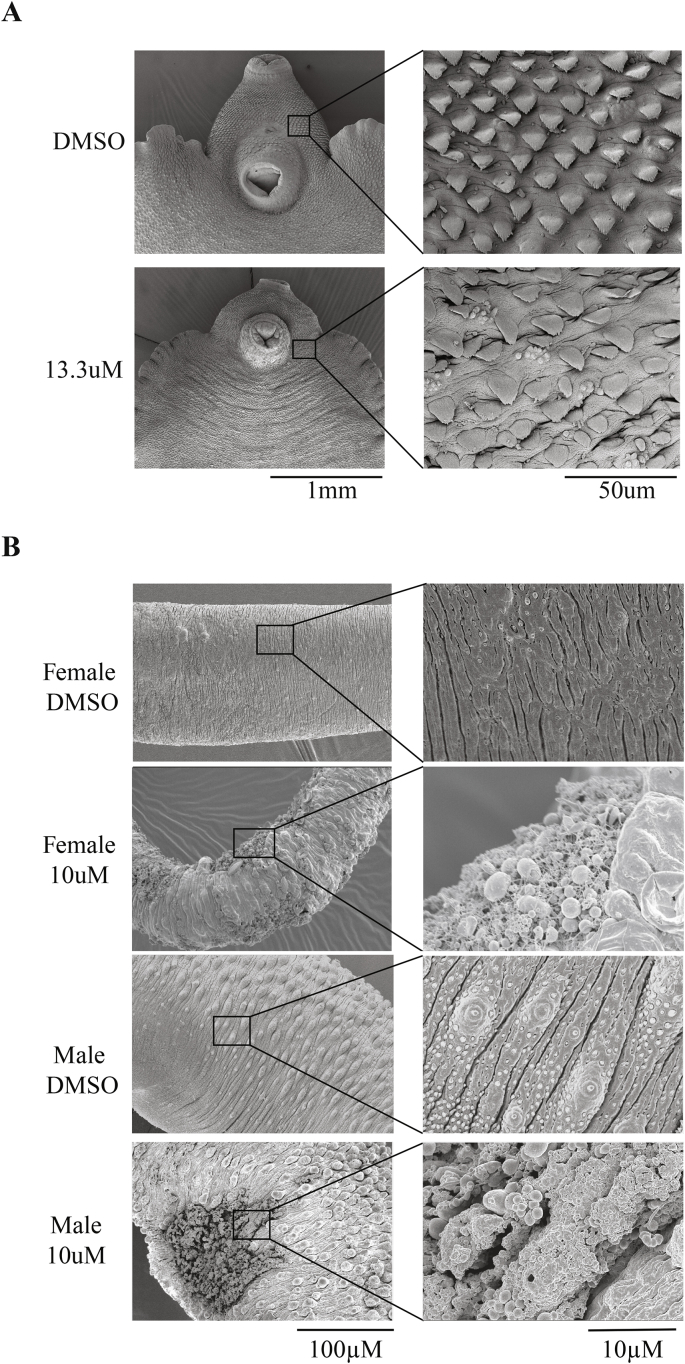
Fig. 6.
The triterpenoid 700015 induces surface damage to both hermaphroditic F. hepatica and dioecious S. mansoni adults. (A) Adult F. hepatica (n = 3) were cultured for 72 h in media containing a sub-lethal concentration (13.3 μM in 0.13% DMSO) of 700015. When compared to control parasites (0.13% DMSO; n = 3) at 72 h, 700015 induced spine erosion and irregular invaginations of the surface tegumental membranes surrounding the acetabulum. (B) Adult S. mansoni worm pairs (males and females; n = 7 pairs) were cultured for 72 h in a sub-lethal concentration (10 μM in 1.25% DMSO) of 700015. When compared to control parasites (1.25% DMSO; n = 7 pairs), 700015 led to tegumental surface disruption and membrane blebbing in 5/7 males and 5/6 females (1 female did not survive the SEM processing).