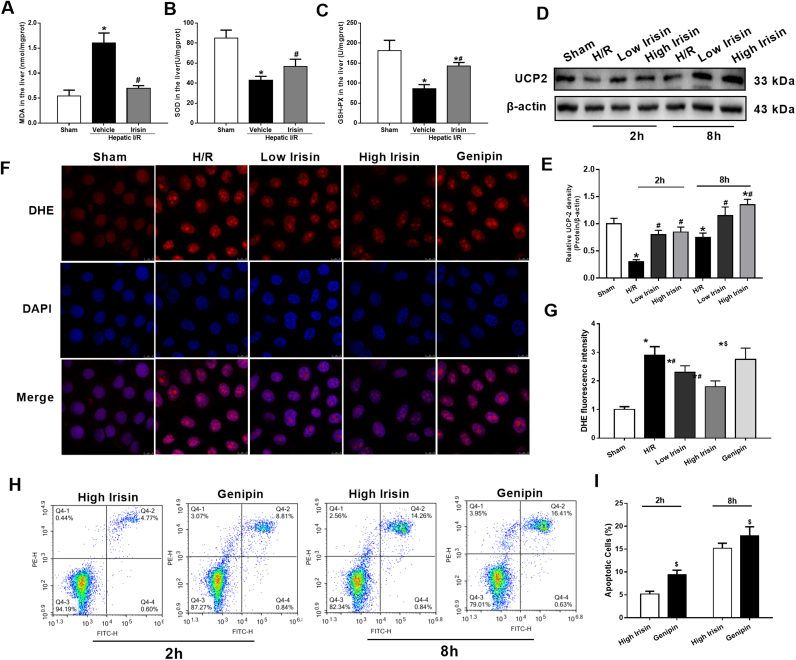
Fig. 7.
Treatment with exogenous irisin reduces oxidative stress after hepatic ischemia-reperfusion (I/R). Irisin treatment in mice was conducted by intravenous administration (250 μg/kg, a single dose) at the beginning of reperfusion. The liver tissues were harvested at 24 h after reperfusion. A-C, the malonaldehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH) levels in the liver in each group, respectively. n = 6, mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05 versus sham group, #P < 0.05 versus vehicle group. D and E, Western blot analysis of UCP 2 expression in HL-7702 cells at 2 h and 8 h after reoxygenation; F and G, DHE fluorescence staining and its fluorescence intensity of HL-7702 cells at 2 h after reoxygenation; H and I, Flow cytometry analysis of HL-7702 cell apoptosis percentage at 2 h and 8 h after reoxygenation. n = 3, mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05 versus sham group, #P < 0.05 versus H/R group, $P < 0.05 versus high irisin group.