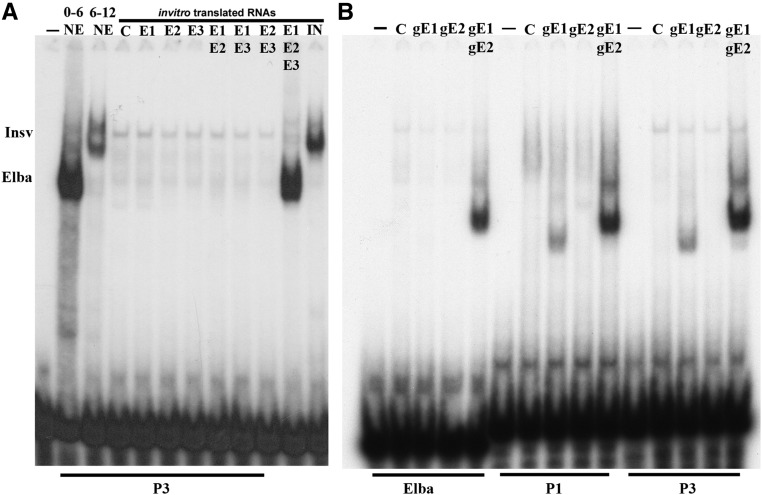
Figure 4.
In vitro-translated Elba and Insv proteins. (A) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) of probe P3 using staged nuclear extracts or in vitro-translated RNAs, as indicated. (−) no nuclear extracts, 0–6 and 6–12: staged nuclear extracts. Rabbit reticulocyte translation mix with no added mRNA (C) or with RNAs encoding the proteins as indicated: E1 (Elba1), E2 (Elba2), E3 (Elba3), and Insv (Insensitive), either alone or in different combinations. (B) EMSA experiments with in vitro-translated GST-Elba1/Elba2 BEN domains and the Elba, P1, and P3 probes. –, no reticulocyte translation mix; C, reticulocyte translation mix, no RNAs; gE1, reticulocyte translation mix primed with an RNA encoding the GST-Elba1CBEN protein; gE2, reticulocyte translation mix primed with an RNA encoding the GST-Elba2CBEN protein; gE1/gE2, reticulocyte translation mix primed with an RNA encoding the GST-Elba1CBEN and GST-Elba2CBEN proteins. Note that gE1 (GST-Elba1CBEN) can bind to the P1 and P3 probes, but not to the Elba probe on its own.