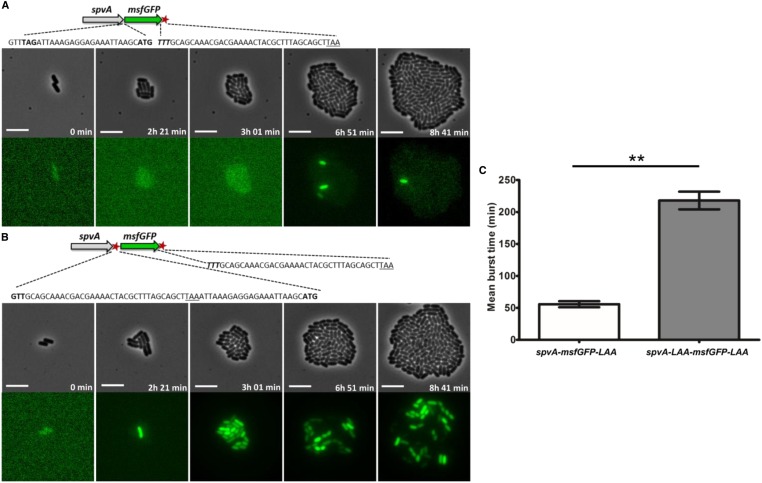
Figure 7.
Images of a time-lapse fluorescence microscopy recording of the growth of a representative microcolony of the (A) S. typhimurium ATCC14028s spvA-msfGFP-LAA and the (B) S. typhimurium ATCC14028s spvA-LAA-msfGFP-LAA strain, showing different PspvA bursting dynamics. (A) Schematic of the S. typhimurium ATCC14028s spvA-msfGFP-LAA strain with the ssrA tag shown as a red asterisk. The junction site between spvA and msfGFP is shown in more detail with the TAG stop codon of SpvA (shown in bold), followed by the ribosome biding site (RBS) and ATG start codon of msfGFP (shown in bold). The 3′ end of msfGFP constitutes of the penultimate TTT codon of msfGFP (shown in bold and in italics), followed by the ssrA degradation tag sequence, and a TAA stop codon (underlined). (B) Schematic of the S. typhimurium ATCC14028s spvA-LAA-msfGFP-LAA strain with the ssrA tags shown as red asterisks. The junction site between spvA and msfGFP is shown in more detail with the penultimate GTT codon of SpvA (shown in bold) followed by the ssrA degradation tag sequence, a TAA stop codon (underlined), and the RBS and ATG start codon of msfGFP (shown in bold). The 3′ end of msfGFP is identical to the one described in A. (C) Mean burst times of the spvA-msfGFP-LAA strain and the spvA-LAA-msfGFP-LAA strain. The burst time was defined as the time in which an individual cell showed an msfGFP signal that exceeded the background levels of OFF cells until this signal faded and returned to background levels again. The mean burst times and SEM for two biological replicates are shown and an unpaired t-test was performed to test for statistical significance (** P < 0.01). The strains were grown to stationary phase in ISM and subsequently seeded and monitored on ISM agarose pads at 37° for the time indicated. The pixel intensities between A and B, and in the different frames, are not comparable and the images are merely a qualitative illustration of the bursting process. The image panels represent the phase contrast channel and the GFP fluorescent channel. Bar, 5 µm.