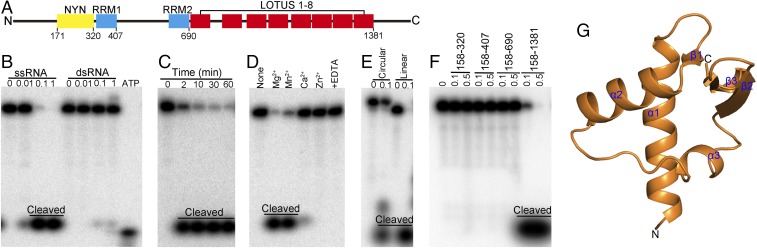
Fig. 1.
In vitro RNase activity assay of MARF1 and the crystal structure of the MARF1-LOTUS domain. (A) Schematic illustration of the domain architecture of M. musculus MARF1. It contains an N-terminal NYN domain (residues 171–320), two central RRM domains (residues 329–407 and 609–690 for RRM1 and -2, respectively), and eight C-terminal repeats of the LOTUS/OST-HTH domain (residues 691–1381). (B) Dose-dependent cleavage of ssRNA but not dsRNA by MARF1. The 5′ 32P-labeled 49-nt ssRNA or dsRNA was incubated with various doses (0.00–1.00 μM) of MARF1 at 37 °C for 5 min. Free [32P]ATP was loaded in the far right lane as a marker. (C) Time-dependent cleavage of ssRNA by MARF1. The 49-nt 32P-ssRNA was incubated with MARF1 (0.05 μM) at 37 °C for 1–60 min. (D) Effect of divalent cations and their chelator on the cleavage activity of MARF1. The 49-nt 32P-ssRNA was incubated with MARF1 (0.05 μM) in solution containing different bivalent cations and/or EDTA at 37 °C for 5 min. (E) The cleavage activity of MARF1 toward linear and circular ssRNA. The 49-nt 32P-ssRNA or circular ssRNA was incubated with or without 0.1 μM of MARF1 at 37 °C for 5 min. (F) RNase activity of different domains of MARF1.The 49-nt 32P-ssRNA was incubated with 0.1 or 0.5 μM of different domains of MARF1 at 37 °C for 5 min. (G) The structure of first LOTUS domain of MARF1.