Fig. 2.
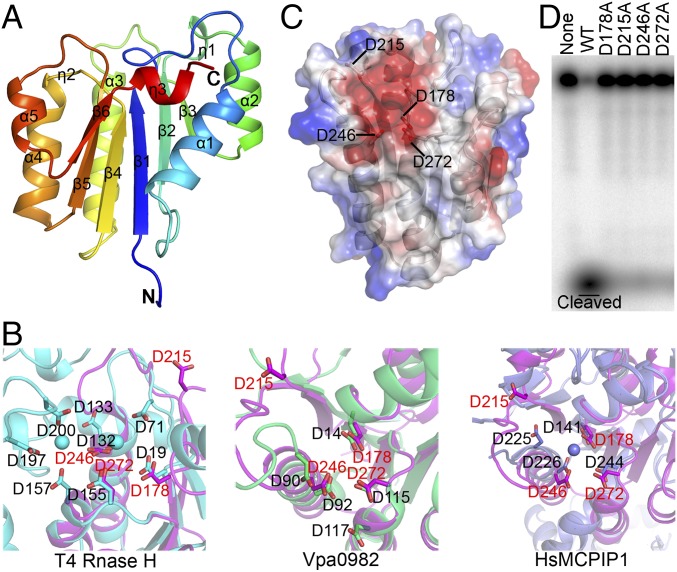
Crystal structure and mutagenic analysis of the NYN domain of MARF1. (A) Cartoon diagram of the overall structure of the NYN domain. The secondary structure elements are labeled. (B) Superimposition of the conserved amino acids of the MARF1-NYN structure (magenta) on the PIN domain of T4 RNase H (cyan) (Left), VPa0982 (green) (Center), and MCPIP1(slate) (Right). (C) Electrostatic surface potential analysis of the NYN structure. Conserved residues D178, D215, D246, and D272 are in the negatively charged pocket. (D) In vitro RNase activity assay of WT and mutant MARF1 in which the conserved aspartate residues (D178, D215, D246, and D272) were mutated individually into alanine.