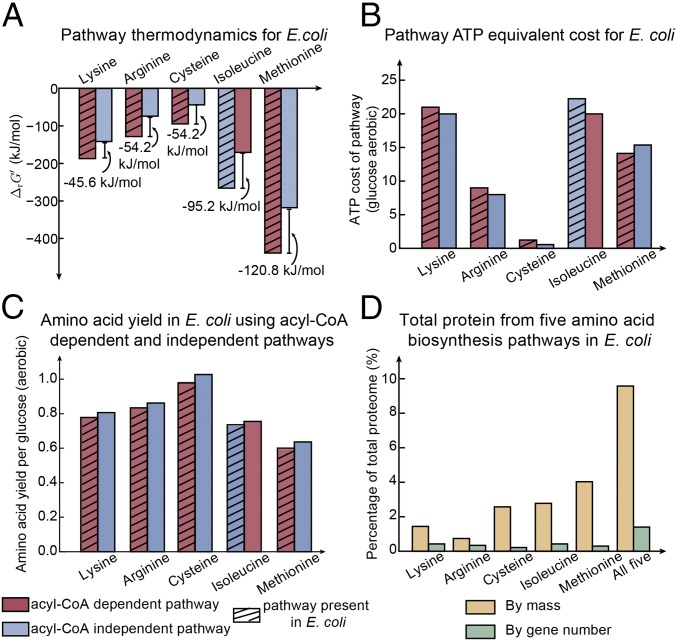
Fig. 2.
Thermodynamics and cofactor-use efficiency of alternative biosynthetic pathways in E. coli. (A) Gibbs energies of reaction () of acyl-CoA–dependent and –independent alternative pathways using E. coli in vivo metabolite concentrations. (B) ATP equivalent cost of acyl-CoA–dependent and –independent pathways calculated from an E. coli metabolic model grown on glucose aerobically. (C) Amino acid yield from acyl-CoA–dependent and –independent pathways simulated using the E. coli metabolic model grown on glucose aerobically. (D) The proteins from five amino acid biosynthesis pathways in terms of fraction in mass and gene number of the total proteome in E. coli.