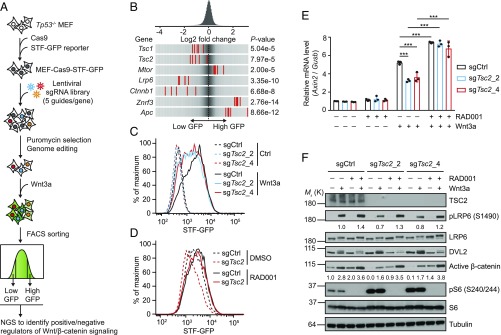
Fig. 1.
A genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screening reveals that mTORC1 signaling negatively modulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling. (A) Workflow of the CRISPR-Cas9 screening process. STF-GFP reporter activity was induced by Wnt3a stimulation overnight, allowing an ideal window for identifying both positive and negative regulators of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. (B) Frequency histograms of sgRNAs identified in the low GFP or high GFP population. sgRNAs targeting indicated genes are shown by the red lines. (C) Deletion of TSC2 decreases the STF reporter activity, assessed by flow cytometry analysis of GFP. (D) RAD001 (50 nM) increases the STF reporter activity and rescues TSC2-deletion–induced reduction of STF reporter activity in the presence of Wnt3a, assessed by flow cytometry analysis of GFP. (E) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Axin2 mRNA level (relative to Gusb). Data shown as mean ± SD for n = 3 independent experiments; significance tested using ANOVA; ***P < 0.001. (F) Immunoblots of indicated proteins for the same cells and treatments as described in E. Densitometry quantification of pLRP6 and active β-catenin are shown.