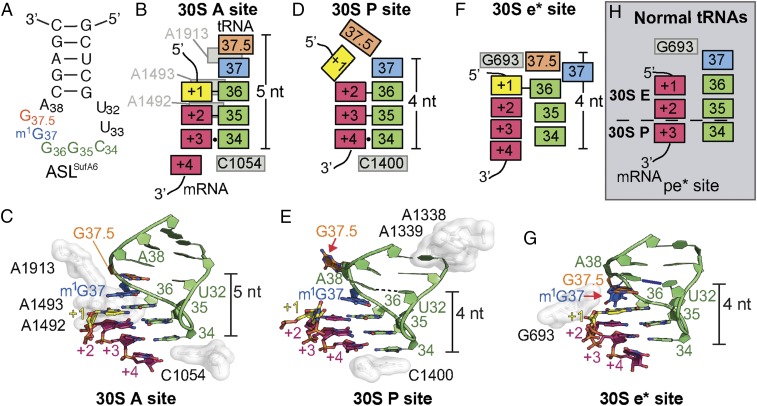
Fig. 2.
Interaction of frameshift-prone tRNASufA6 with the tRNA-binding sites on the ribosome. (A) Secondary structure of ASLSufA6 with the anticodon nucleotides (green), the inserted nucleotide G37.5 (orange), and the modified G37 (blue). (B and C) Schematic (B) and structure (C) of the codon–anticodon interaction in the A site. The anticodon and mRNA are surrounded by 16S rRNA nucleotides A1492/93, A1913, and C1054 (white), which aid correct tRNA selection. ASLSufA6 forms a 5-nt stack and is decoded in the zero frame despite containing an additional anticodon loop nucleotide, G37.5 (orange) (PDB ID code 4L47). Watson–Crick base pairs between the first two interactions of the anticodon and the codon (+1–36 and +2–35) are shown with a black bar, and the +3–34 wobble interaction is shown with a circle (B). There is no interaction between U32 and A38. (D and E) In the P site, the anticodon and codon are minimally monitored, and instead 16S rRNA nucleotides A1338/9 (white) recognize the anticodon stem and C1400 packs beneath the +4–34 base pair. In this relaxed state, ASLSufA6 forms a 4-nt stack by base-flipping G37.5 (red arrow in E) and engages the mRNA codon nucleotides +2, +3, and +4 in the new +1 frame. This movement also reestablishes the U32-A38 pairing (shown with a dotted line). Watson–Crick base pairs between the first two interactions of the anticodon and the codon (+2–36 and +3–35) are shown with a black line, and the +4–34 wobble interaction is shown with a circle (D). (F and G) Frameshift-prone tRNASufA6 is biased toward the E site, adopting a new position (e*) on the 30S that pulls the mRNA codon by one nucleotide into the E site. Additional remodeling of the ASL ejects m1G37 (red arrow in G) to maintain the 4-nt stack and the U32-A38 pairing (show with a blue line). The single interaction between the codon and the anticodon is denoted as a black bar (+1–36) in F. (H) Comparison of a 70S·EF-G translocation intermediate state containing a pe/E tRNA (PDB ID code 4V9L) reveals that during canonical translocation, there is space between 16S rRNA nucleotide G693 and the +1 mRNA of the codon. This allows for the full accommodation of the E site codon on completion of translocation. The anticodon is pulled away from the mRNA, as shown by the lack of Watson–Crick base pair interactions. The dotted line signifies the barrier between the 30S E and P sites.