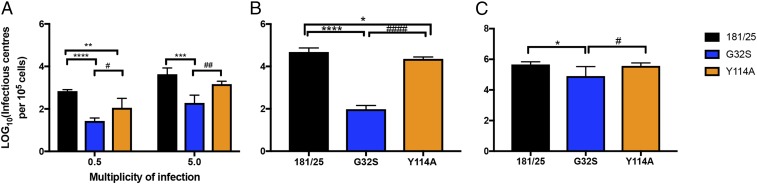
Fig. 2.
nsP3MD mutations affecting ADP ribosyl binding and hydrolase activities differentially affect the initiation of infection. (A) Infectious center assays for NSC34 cells infected at MOIs of 0.5 and 5 with CHIKV 181/25 (WT) and nsP3MD mutants G32S or Y114A. Infected cells were trypsinized, viable cells were counted, and serially diluted cells were plated on Vero cells to identify virus-producing cells by plaque assay. (B and C) Infectious center assays for NSC34 (B) and BHK21 (C) cells after electroporation of 10 μg of viral RNA transcribed in vitro from full-length clones of 181/25 and nsP3MD G32S and Y114A mutants into 105 cells that were plated onto subconfluent monolayers of BHK21 cells to identify virus-producing cells by plaque formation. The data are presented as log10 infectious centers per 105 cells. Each value represents the average ± SD from three independent experiments; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 (WT vs. G32S/Y114A); #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01, ####P < 0.0001 (Y114A vs. G32S).