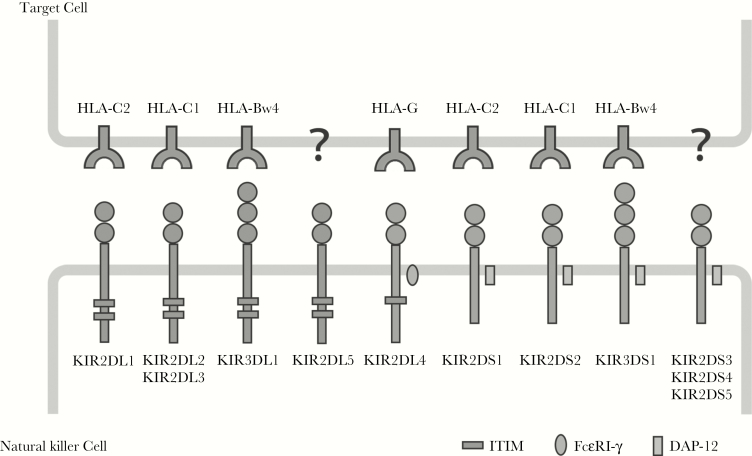
Figure 1.
Killer immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) proteins are classified by the number of extracellular immunoglobulin domains (2D or 3D) and by whether they have a long (L) or short (S) cytoplasmic domain. Inhibitory KIRs and KIR2DL4 have immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) in their cytoplasmic domains. Activating KIRs possess a basic amino acid in the transmembrane domain, which allows interactions with the accessory molecule DAP-12, delivering activating signals through its immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activating (ITAM) motif. The ligands for several KIR proteins are subsets of HLA class I proteins. KIR2DL4 has a charged amino acid and ITIM motifs, and it interacts with the accessory protein FcεRI-γ, which sends an activating signal via its ITAM similar to DAP-12. Note that HLA-Bw6 alleles are not known to be KIR ligands.