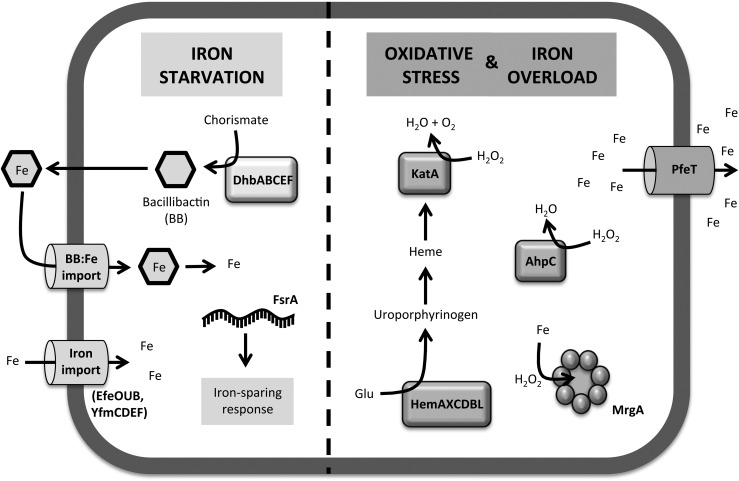
FIG. 1.
Iron-related stress responses in Bacillus subtilis. Schematic summary of the response mechanisms in B. subtilis to different types of iron-related stresses. When cells are subjected to iron starvation, cells express genes involved in iron acquisition, which encode iron importers and siderophore biosynthesis enzymes. Cells also express the small RNA FsrA, which targets post-transcriptional inhibition of low-priority iron requiring enzymes, thus implementing the iron sparing response. Under conditions of oxidative stress, cells induce expression of peroxide detoxifying enzymes (KatA and AhpC) and their cofactors (HemAXCDBL), as well as enzymes that have an impact on cellular iron levels, such as the iron sequestration ferritin-like protein (MrgA) and the P1B4-type ATPase iron efflux pump PfeT. Note that under iron overload conditions, PfeT and (to a lesser extent) MrgA also confer resistance to excess iron. AhpC, alkyl hydroperoxide reductase; Fe, iron; KatA, catalase.