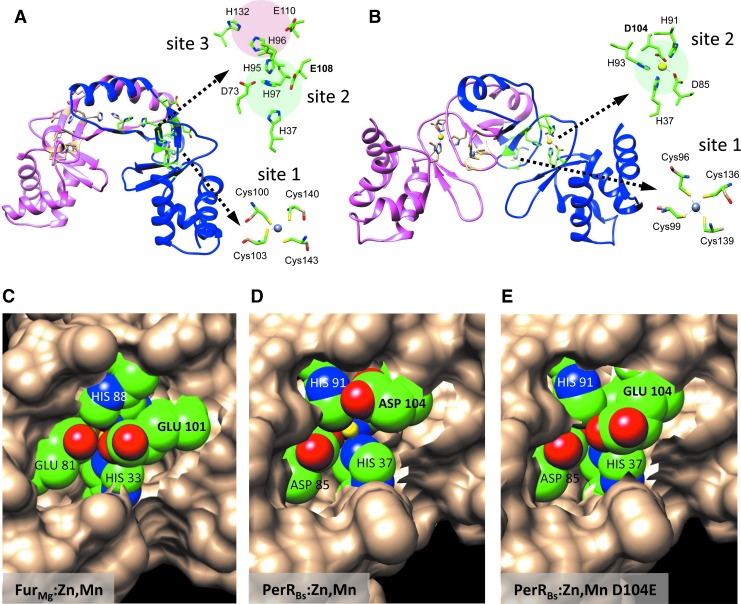
FIG. 2.
Fur and PerR structures. (A) FurBs structural homology model based on the Streptomyces coelicolor Zur structure (PDB: 3mwm; sequence identity: 33.3%) (102). This FurBs model shows the predicted homodimer in its holo-form. Close-up views of its three conserved metal-binding sites are provided in stick form. Site 1 is a Cys-rich pocket that binds a structural Zn2+ atom to provide protein stability to the dimer. Sites 2 and 3 comprise the iron-sensing site (shown without metal atoms), where site 2 seems to play a primary role in triggering the conformational changes required for DNA binding [figure adapted from (78)]. (B) PerRBs crystal structure bound with Mn2+. A close-up of the metal-sensing site (site 2) and the structural site (site 1) is depicted in stick form (PDB code: 3F8N). (C) Crystal structure of FurMg:Zn,Mn (PDB code: 4RAZ) showing a close-up of binding site 1, which is analogous to site 2 in FurBs and in PerRBs. Mn2+ is not easily accessible. (D) Crystal structure of PerRBs:Zn,Mn (PDB code: 3F8N) showing a close-up of binding site 2. Mn2+ is easily accessible. (E) Crystal structure of PerRBs:Zn,Mn showing a close-up of binding site 2 with conserved Asp104 residue mutated into a Glu. Mn2+ is completely occluded (Mn2+ = yellow; nitrogen atom = blue; oxygen atom = red; carbon atom = green). Asp, aspartate; Cys, cysteine; Fur, ferric uptake regulator; Glu, glutamate; His, histidine; Mn, manganese; Zn, zinc.