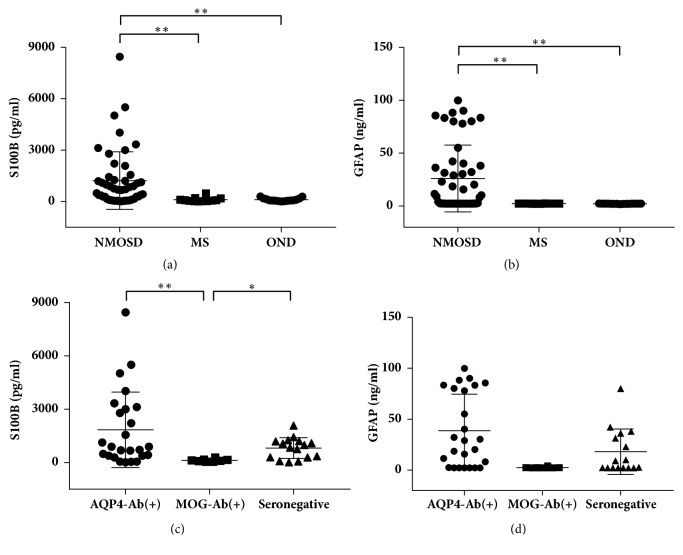
Figure 1.
CSF levels of S100B and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), multiple sclerosis (MS), other noninflammatory neurological diseases (OND), and NMOSD subgroups. (a) Patients with NMOSD had significantly higher levels of CSF-S100B than those with MS and OND. (b) NMOSD patients had significantly higher levels of CSF-GFAP than MS and OND patients. (c) The CSF-S100B levels in aquaporin-4 antibody-positive NMOSD [AQP4-Ab (+)] and seronegative NMOSD were significantly higher than those in myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-positive NMOSD [MOG-Ab (+)]. (d) The CSF-GFAP levels were higher in AQP4-Ab (+) patients than those in MOG-Ab (+) patients but did not reach a significant difference. Each dot represents a biomarker level in a subject. Lines and whiskers represent mean values and standard deviation, respectively. ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01 represent statistical significance in the Mann–Whitney U test with Bonferroni correction.