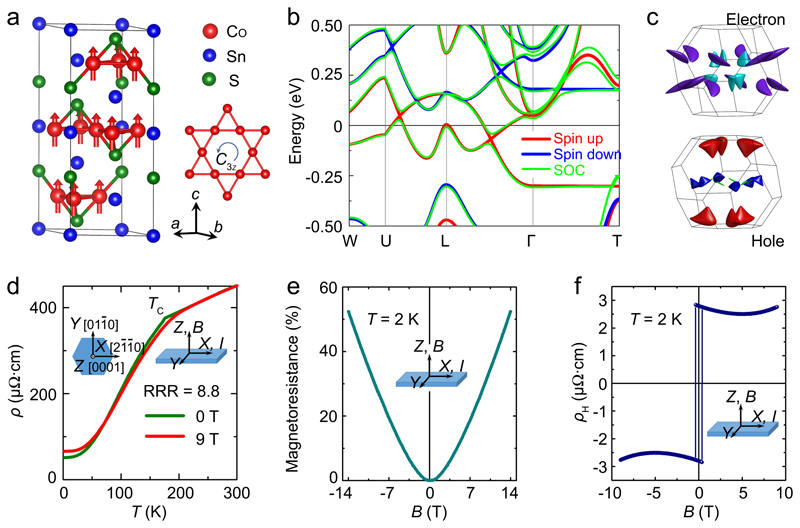
Figure 1. Crystal and electronic structures of Co3Sn2S2 and the measured electric resistivity.
a, Unit cell in a hexagonal setting. The cobalt atoms form a ferromagnetic Kagomé lattice with a C3z-rotation. The magnetic moments are shown along the c-axis. b, Energy dispersion of electronic bands along high-symmetry paths without and with spin-orbit coupling, respectively. "SOC" denotes "Spin-orbit coupling". c, Fermi surfaces of two bands (upper: electron; lower: hole) under spin-orbit coupling calculations. Different colors indicate different parts of the Fermi surface in the Brillouin zone. d, Temperature dependences of the longitudinal electric resistivity (ρ) in zero and 9-T fields. In zero field, a residual resistance ratio (RRR, ρ300K/ρ2K) value of 8.8 and a residual resistivity of ρ2K ~ 50 μΩ cm is observed. e, Magnetoresistance measured in fields up to 14 T at 2 K, showing a non-saturated positive magnetoresistance. f, Hall data with a non-linear behaviour at high fields, indicating the coexistence of electron and hole carriers at 2 K. All transport measurements depicted here were performed in out−of−plane configuration with I // x // [21̄1̄0] and B // z // [0001]. The x and z axes, respectively, are thus parallel to the a and c ones shown in a.