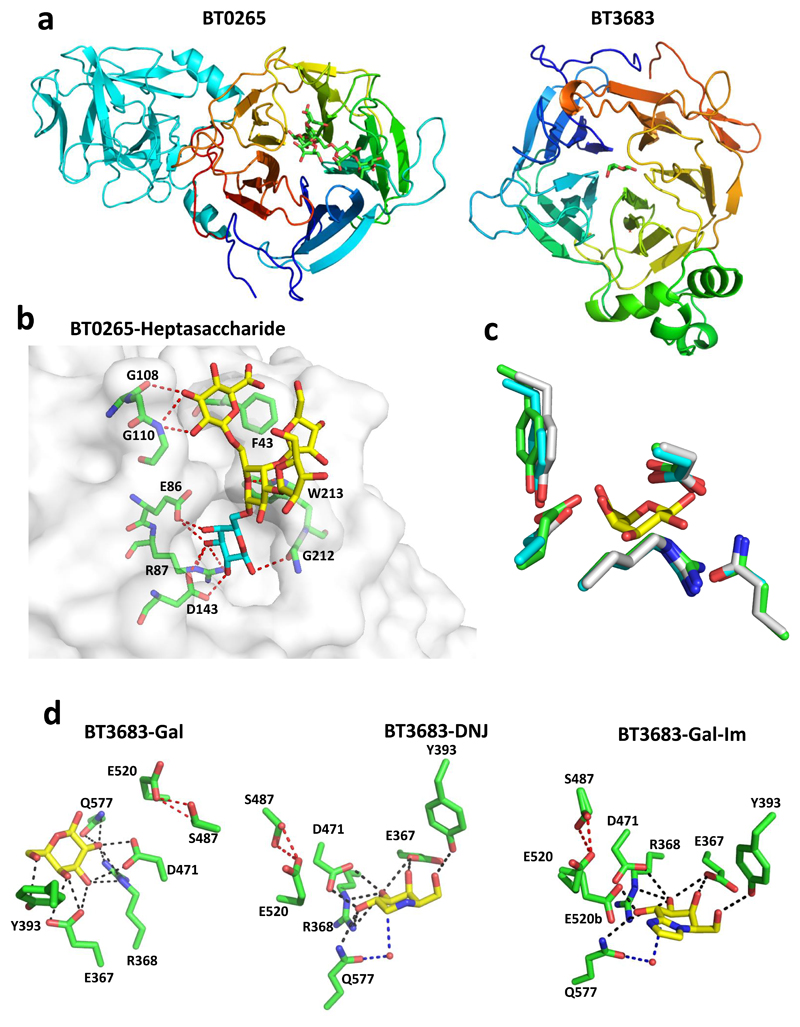
Figure 3. The crystal structure of GH43_24 β1,3-D-galactosidases in complex with ligands.
a, schematic of BT0265 (left) and BT3683 (right) in which the catalytic domains are colour ramped from blue at the N-terminus to red at the C-terminus. The C-terminal β-sandwich domain in BT0265 is coloured cyan. b, shows the solvent exposed surface of BT0265 in complex with the heptasaccharide shown in Supplementary Fig. 3 (terminal α-Gal and α-Rha are not visible). Electron density for the terminal α-Gal was too weak to model the sugar. The red dashes show the polar interactions between the ligand and both side chains and backbone N and O. Residues that make polar contacts with the side chain of the ligand are also shown. c, an overlay of the residues in BT0265 (cyan), BT3683 (green) and the GH43_24 β1,3-galactosidase Cthe_1271 (grey; PDB code 3VSZ) that interact with galactose (yellow) in complex with BT3683. d, BT3683 in complex with galactose (Gal), deoxygalactonojirimycin (DGJ) and galactose-imidazole (Gal-Im). Direct polar interactions between enzyme and ligand are indicated by black dashes and the indirect water-mediated hydrogen bonds in magenta dashes. The red dashed line represents the polar interaction between the catalytic acid (Glu520) and Ser487. The two conformations of Glu520 in the Gal-Im complex is denoted by a and b.