Figure 5: Pharmacological inhibition of RA signaling partially rescues the E8.5-CMEzh2 mutant phenotype and restores the PM-derived bones.
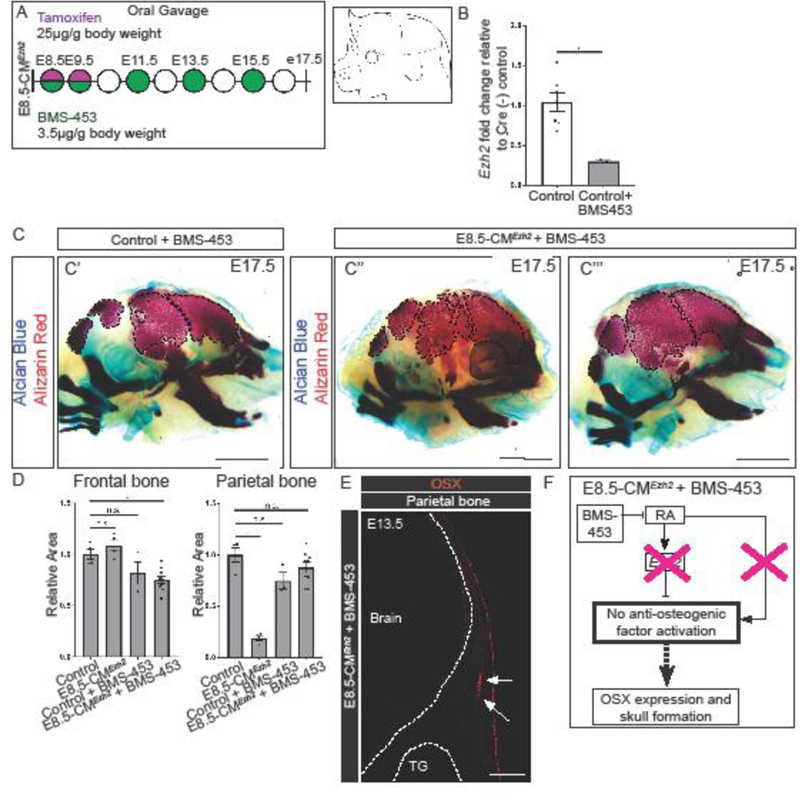
(A) Gavage regimen for tamoxifen and RA-antagonist BMS-453 in E8.5-CMEzh2 mutants and schematic of obtaining manually enriched CM without the ectoderm. (B) RT-qPCR for Ezh2 in Cre- control and BMS-453 treated embryos from E13.5 manually enriched CM. (C) Skeletal staining of E17.5 3.5µg/gm BMS-453 treated Ezh2 mutants. C' and C'' represent two different litters. Alcian blue marks cartilage and alizarin red marks bone (scale bar = 2mm). (D) Quantification of the Alizarin Red stained area outlined in (C) using ImageJ/Fiji. (E) Immunofluorescence of OSX in the parietal bone at E13.5. Arrows indicate partial restoration of OSX (scale bar = 200µm). (F) Schematic with proposed model by which, in the absence of Ezh2, inhibition of RA-signaling prevents the activation of the anti-osteogenic genes restoring OSX expression and skull bone formation.
