Figure 1. Proteomics of Influenza Polymerase Subunit PA Reveal Interactions with RNA Exosome.
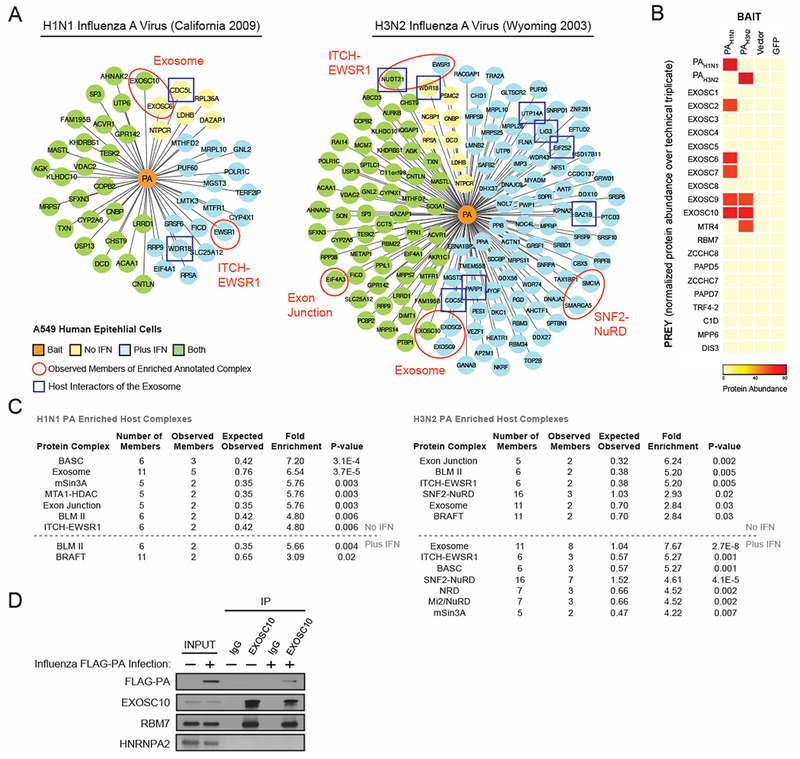
(A) IAV polymerase acidic protein (PA) from (left) H1N1 (California 2009) or (right) H3N2 (Wyoming 2003) with C-terminal 2xStrep tags were expressed in A549 cells and subjected to affinity purification and mass spectrometry (AP-MS) in biological triplicate with and without interferon pre-treatment. Human proteins (prey) significantly enriched after PA purification (orange - bait) relative to vector and GFP-2xStrep control samples are depicted (yellow - without interferon, blue – with interferon, green – both with and without interferon). Known exosome interacting partners are boxed in blue. (B) Heatmap depicting the relative protein abundance of bait proteins and exosome subunits across biological triplicates (without interferon) in the AP-MS samples. (C) Significantly enriched protein complexes from the CORUM database are annotated with pertinent complex members circled and labeled in red in the above networks. (D) A549 cells were infected with a PA-FLAG-tagged IAV for 10 hours. Endogenous EXOSC10 was immunoprecipitated from cell lysate. Co-immunoprecipitated proteins were detected by immunoblot. See also Figure S1 and Table S1
