Figure 5. Synthesis of host:viral chimeric RNAs is dependent on the Nuclear RNA Exosome.
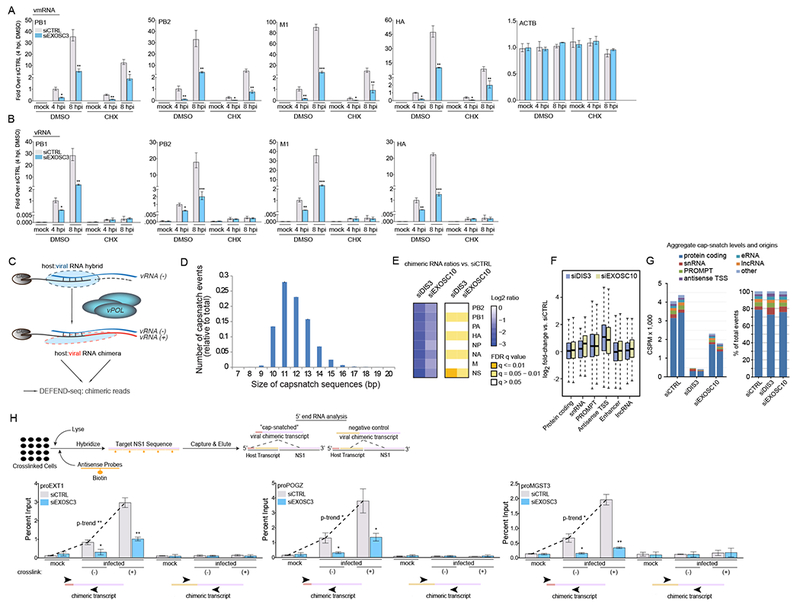
(A-B) qPCR of host mRNA and IAV mRNA (A), and RNA levels (B) in A549 cells infected with PR8 at the indicated time points. Cells were transfected with a siRNA targeting EXOSC3 or a non-targeting siRNA (siCTRL) and treated, at the time of infection, with cycloheximide (CHX) or DMSO.
(C) Schematic of how the synthesis of each IAV mRNA requires the formation of a host:viral RNA hybrid followed by polymerization to generate the (+) strand from the viral (−) strand template. The plus strand (viral mRNA) is then a chimeric RNA formed by a 9-16mer of cellular RNA (see panel D for size distribution).
(D) Length distribution of cellular transcript fragments (snatched RNA) found at the 5’ ends of viral mRNA in PR8 infected A549 cells at 4 hours post-infection.
(E) Heat map of average expression changes of positive-stranded host:viral chimeric mRNAs in A549 cells transfected with siRNAs targeting DIS3 or EXOSC10, or a non-targeting siRNA (siCTRL). Cells were infected with PR8 for 4 hours and expression changes reflect the fold-change ratio between either siDIS3 or siEXOSC10 and siCTRL conditions.
(F) Box plots of the log2 fold-change in expression for different transcript biotypes in uninfected A549 cells transfected with siRNAs as used in E, compared to siCTRL. PROMPTs were defined as transcripts identified between 1 and 2.5 kb upstream of annotated transcription start sites (TSS). Antisense TSS transcripts were identified in a 500 bp region upstream of annotated TSS features.
(G) Left: Cap-snatch per-million events across cellular gene categories in A549 cells (from panel E). Duplicates are shown. Right: Proportional distribution of cap-snatch origins according to cellular transcript biotype.
(H) Top: RNA antisense purification (RAP) experimental strategy for IAV NS1 segment purification. Bottom: RAP-qPCR of host:influenza virus chimeric mRNA levels in A549 cells infected with PR8 before (mock) or 6 hours post-infection (infected). Cells were transfected with a siRNA targeting EXOSC3 or a non-targeting siRNA (siCTRL). At time of collection, cells were cross-linked (+) or left native (−). Primers spanning the internal region of the viral segment and the 5’ or internal portion of the indicated PROMPTs were used to amplify chimeric RNAs.
Statistical analyses between datasets were performed with a two-tailed Student’s t-test, adjusted with a Holm-Bonferroni test for sequential comparisons. For panels A-B, H, *p<.05, **p<.005, and ***p<.0005. Error bars indicate SD from triplicate (A-B) and duplicate experiments (D-H).
See also Figure S5
