Figure 6. Models for the co-transcriptional interference of influenza virus with RNAPII and the RNA Exosome.
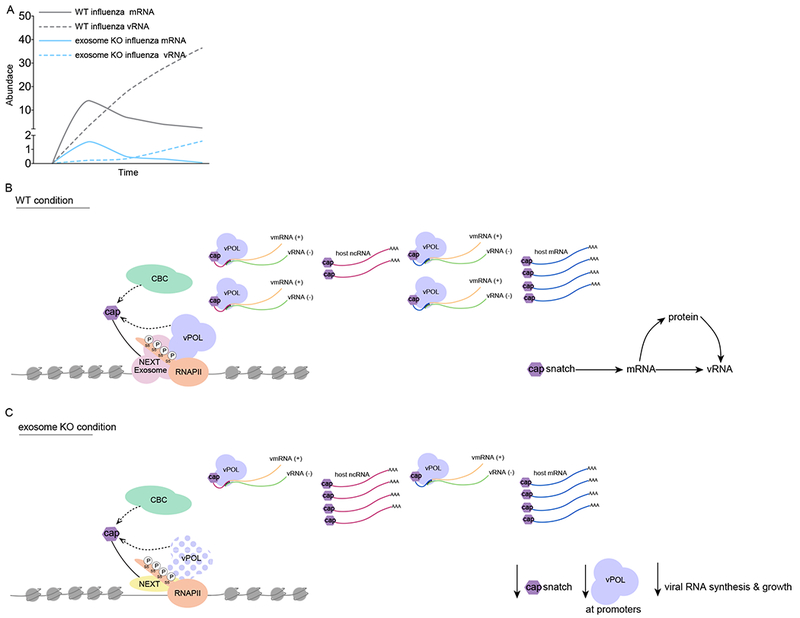
(A) Model displaying IAV RNA and mRNA kinetics over the time of an infection in exosome proficient (gray) and deficient (blue) cells.
(B) IAV cap-snatching model in exosome proficient cells. IAV polymerase (vPOL) accesses host ncRNA and mRNA in kinetic competition with RNAPII- and RNA exosome-dependent capbinding complex (CBC) dynamics, which control productive elongation of mRNA and co-transcriptional maturation at ncRNA loci.
(C) IAV cap-snatching model in exosome deficient cells. IAV polymerase (vPOL) access to host ncRNA and mRNA is impaired because of reduced targeting of the viral polymerase to promoters and by defects in promoter-proximal RNAPII activity. This results in stabilization of ncRNA and TSS-RNA and a concomitant reduction of chimeric transcripts.
See also Figure S6
