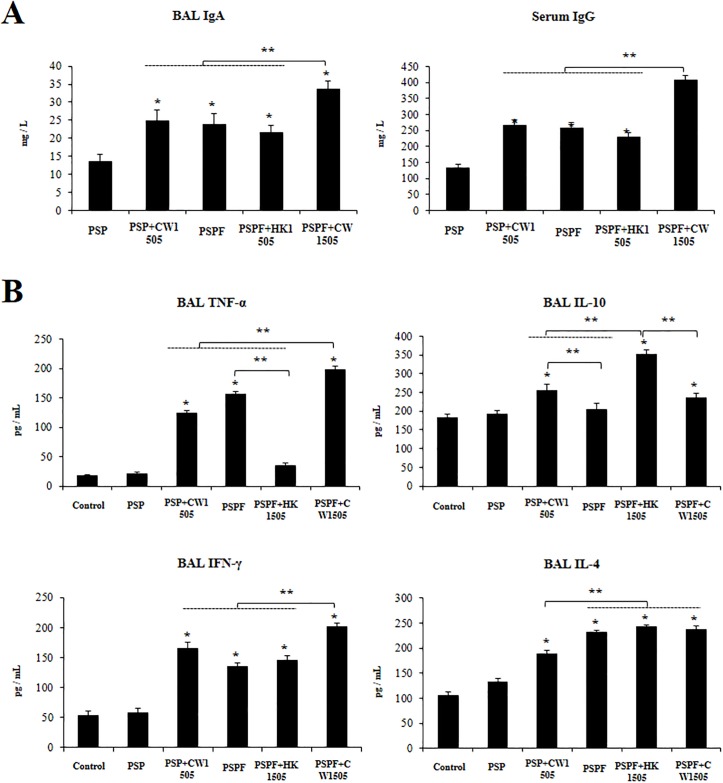
Fig 8. Immune response induced by the immunization with recombinant chimeric pneumococcal protein PSPF (PsaA- Spr1875-PspA-FliC) or PSP (PsaA- Spr1875-PspA) plus non-viable Lactobacillus rhamnosus CRL1505 or its cell wall in infant mice.
Swiss albino infant mice (3-week old) were immunized by nasal route with PSPF or PSP (20 μg in 25 μl of sterile PBS), PSPF (20 μg) plus heat-killed L. rhamnosus CRL1505 (HK1505) (108 cells), or PSPF or PSP (20 μg) plus the cell wall from L. rhamnosus CRL1505 (CW1505) (8 μg) in 25 μl of sterile PBS on days 0, 14 and 28. A) Five days after the last immunization, serum and broncho-alveolar lavage (BAL) samples were obtained for the determination of IgA and IgG specific antibodies. Concentrations of specific antibodies in sterile PBS-treated control mice samples were below the detection limit. B) One day after the last immunization BAL samples were obtained for the determination of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interferon (IFN)-γ, interleukin (IL)-4, and IL-10 concentrations. Each experimental group consisted of 3 mice per group and experiments were performed in triplicate (n = 9). Results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Differences were considered significant at p < 0.05 when compared with animals immunized with PSP only (*) or with the indicated groups (**).