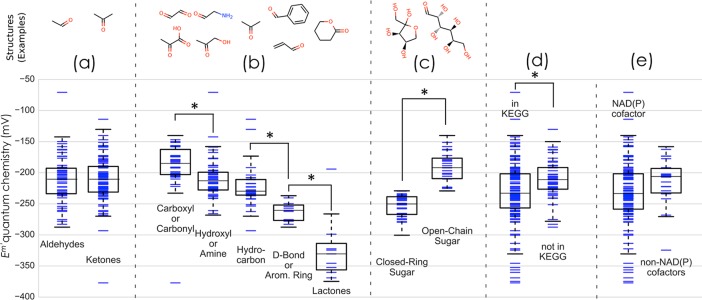
Fig 4. Comparison between the redox potentials of sub-groups for reactions in the G2 category (carbonyl to hydroxycarbon reductions).
(A) Aldehydes vs. ketones (non-statistically significant Δ <E′m>); (B) nearest-neighbor functional group (all subgroups have statistically significant Δ <E′m>, p<0.005, except hydroxyl/amine and hydrocarbon) (C) closed-ring sugar reduction to open-chain vs. open-chain sugar reduction to open-chain (statistically significant Δ <E′m>, p<10–5), (D) natural reactions appearing in KEGG vs. non-natural reactions (statistically significant Δ <E′m>, p<0.005) (E) natural reactions that only use NAD(P) as redox cofactor vs. those that use alternative cofactors (cytochromes, FAD, O2, or quinones) (non-statistically significant Δ <E′m>, p = 0.03).