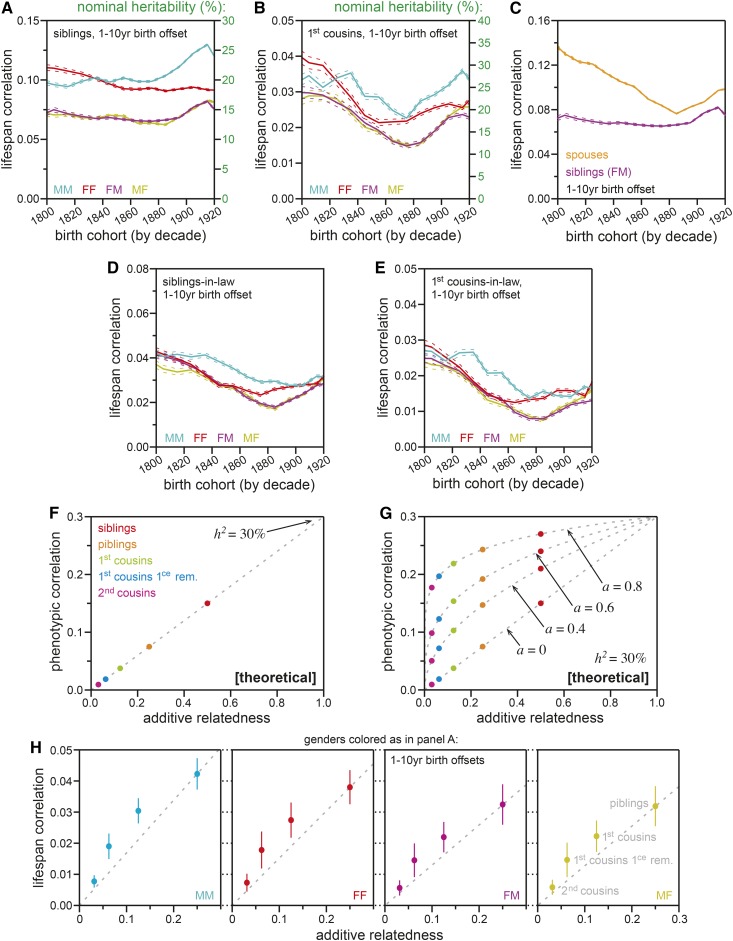
Figure 3.
Life span correlations with in-law relatives and patterns of remote relative correlations reveal substantial assortative mating for factors affecting longevity. (A) Life span correlations for siblings (y-axis); x-axis: the birth-decade of the proband. The sibling of each proband was required to be born 1–10 years prior to that proband. Gender-specific correlations between male–male (MM; cyan), female–female (FF; red), female–male (FM; magenta), and male–female (MF; yellow) sibling-pairs were calculated separately. Dotted lines indicate estimate SE. The nominally estimated heritability values are shown on the right-hand y-axis. (B) Life span correlations for first cousins, calculated and plotted as in (A). (C) Life span correlations for female–male sibling-pairs [FM; magenta; reproduced from (A)] and spouse-pairs (orange), calculated and plotted as in (A). (D) Life span correlations for siblings-in-law, calculated and plotted as in (A). (E) Life span correlations for first-cousins-in-law, calculated and plotted as in (A). (F) A theoretical plot illustrating the linearity between additive relatedness (x-axis) vs. phenotypic correlation (y-axis) that is assumed across relative types by the nominal heritability model (see Supplemental Text, section 2). Dots indicate particular relationship types; the dashed gray line indicates the continuous function. (G) A theoretical plot illustrating the amplifying effects of assortative mating (a) on phenotypic correlations. Axes as in (F). For various values of a, dots indicate particular relationship types [colored as in (F)]; dashed gray lines indicate the continuous functions (see Supplemental Text, section 2). (H) The observed relationships between additive relatedness (x-axis) and life span correlations (y-axis) for four remote relative types, all relatives born 1–10 years prior to the proband. Dots indicate the mean value for decade birth cohorts, 1800–1920. Vertical lines indicate the SD of correlation values across those decades. Each panel displays estimates for a particular gender pair, colored as in (A). Dashed gray lines indicated a nominal (linear) extrapolation through piblings. Siblings are omitted from this plot due to the confounding effects of shared-household environment (see Supplemental Text, sections 1.4 and 2.2).