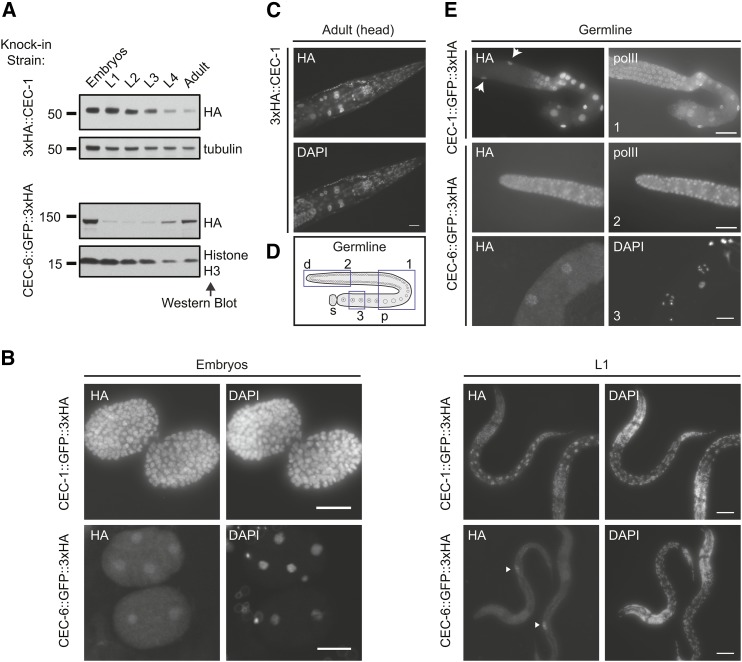
Figure 2.
Distinct expression patterns of C. elegans chromo-domain proteins CEC-1 and CEC-6. (A) Relative expression levels of CEC-1 and CEC-6 across developmental stages. The 3xHA (hemagglutinin) epitope was inserted in-frame at the endogenous locus using clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/Cas9 genome editing (see also Figure S3C). L1–L4, larval stages 1–4. (B) Localization of CEC-1 and CEC-6 by anti-HA tag immunofluorescence in embryos and L1 animals. The arrowheads [(B), lower right] indicate the primordial germ cells (see also Figure S3D). (C) Broad nuclear expression of CEC-1 in the adult head. (D) Schematic of an isolated germline arm indicating three regions depicted in (E). The distal germline is a syncytium, with germ cells surrounding a central canal. d, distal; p, proximal; and s, spermatheca. (E) Expression of CEC-1 and CEC-6 in dissected germlines. The arrows (top panel) indicate nuclei of the somatic gonad cells. Germlines in (C) were costained with an antibody detecting the RNA polymerase C-terminal domain (polII) to control for antibody penetration.