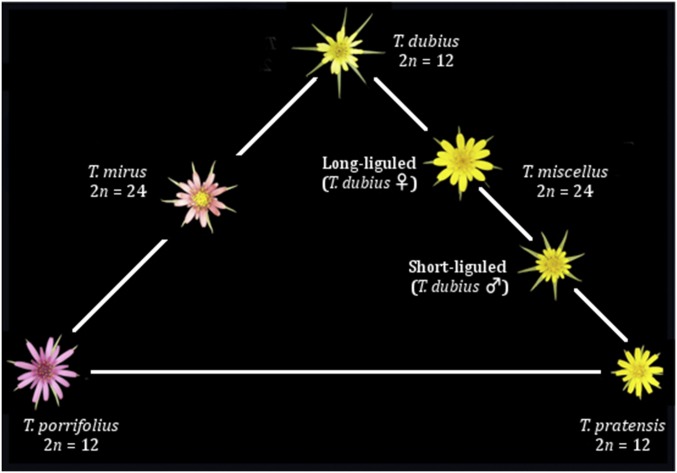
Figure 1.
Tragopogon Triangle. Triangle depicting the relationships between diploid and polyploid Tragopogon species. Diploid individuals occupy the corners of the triangle with polyploids resting between their corresponding diploid progenitors. The polyploid T. mirus is formed with a paternal T. dubius and maternal T. porrifolius. In this study, we are using the short-liguled T. miscellus, which is formed by paternal T. dubius and maternal T. pratensis. There are no naturally occurring polyploids between T. porrifolius and T. pratensis, although these two species do form diploid hybrids in nature.