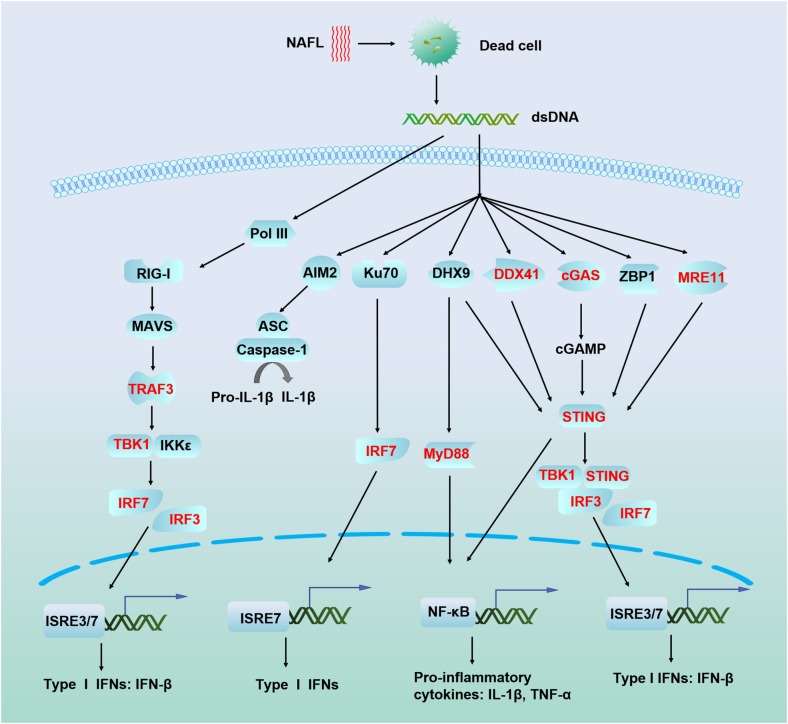
FIGURE 6.
Schematic illustration of nucleic acid recognition and interferon production mechanism of ATRA/NAFL. Dead cells generated by NAFL or ATRA/NAFL released nucleic acid-like dsDNA in the cytoplasm which is sensed by many sensors leading to the production of type I IFNs via adaptors MAVS, STING, and transcriptional factors IRF3 and IRF7. Most DNA sensors like DHX9, DDX41, cGAS, ZBP1, and MRE11 are believed to activate STING, recruit TBK1 to phosphorylate IRF3/IRF7, and then dimerize and enter the nucleus, resulting in the production of type I IFNs. Pol III transcribes dsDNA to synthesize RNA, which is sensed by RIG-I, while RIG-I can be induced and activated by ATRA. RIG-I recruits TRAF3 via MAVS to trigger the activation of the downstream kinases TBK1 and IKK𝜀 and then phosphorylates IRF3 and IRF7, which homodimerize and enter the nucleus to induce the production of type I IFNs. Genes upregulated by ATRA/NAFL are shown in the bold red font. Abbreviations: AIM2, absent in melanoma 2; ASC, PYD and CARD domain containing (PYCARD); cGAMP, 2′3′ guanosine–adenosine monophosphate; cGAS, cyclic GMP–AMP synthase; DDX41, DEAD-box helicase 41; DHX9, DExH-box helicase 9; IFN-β, interferon beta; IKK𝜀, IkB kinase epsilon; IL-1β, interleukin 1 beta; IRF3, interferon regulatory factor 3; IRF7, interferon regulatory factor 7; ISRE, interferon-sensitive response element; Ku70, Lupus Ku autoantigen protein p70; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein; MRE11, meiotic recombination 11 homolog A; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells; Pol III, RNA polymerase III; RIG-I, RA inducible gene-I; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; TBK1, TANK binding kinase 1; TNF-α, Tumor necrosis factor alpha; TRAF3, TNF receptor associated factor 3; ZBP1, Z-DNA binding protein 1.