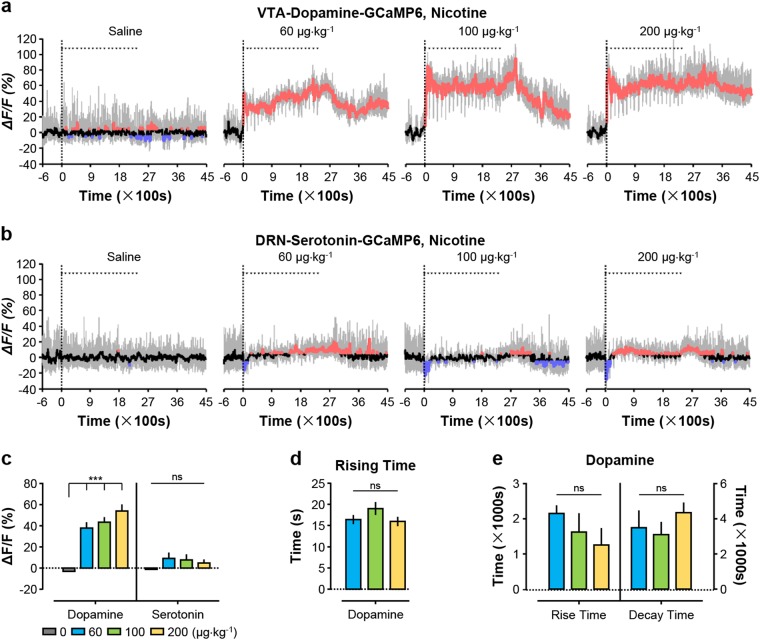
Fig. 2. Nicotine rapidly and strongly activates VTA dopamine neurons but has only modest effect on DRN serotonin neurons.
a, b Representative traces of Ca2+ signals from dopamine neurons and serotonin neurons treated with 20 infusions of nicotine at the indicated doses. c Overall Ca2+ signal intensities during nicotine infusions [n = 6 dopamine mice, F(3, 20) = 27.37, p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test; n = 7 serotonin mice, F(3, 24) = 1.235, p = 0.3188, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test]. d The initiation time of Ca2+ signals following the first infusion of nicotine for VTA dopamine neurons [n = 6 dopamine mice; F(2, 15) = 1.013, p = 0.3866, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test]. e Rise time and decay time of nicotine-evoked Ca2+ signals for VTA dopamine neurons [n = 6 dopamine mice; for rise time F(2, 15) = 1.050, p = 0.3742, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test; for decay time, F(2, 12) = 0.6585, p = 0.5354, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test]. Error bars indicate SEM (c–e). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ns not significant