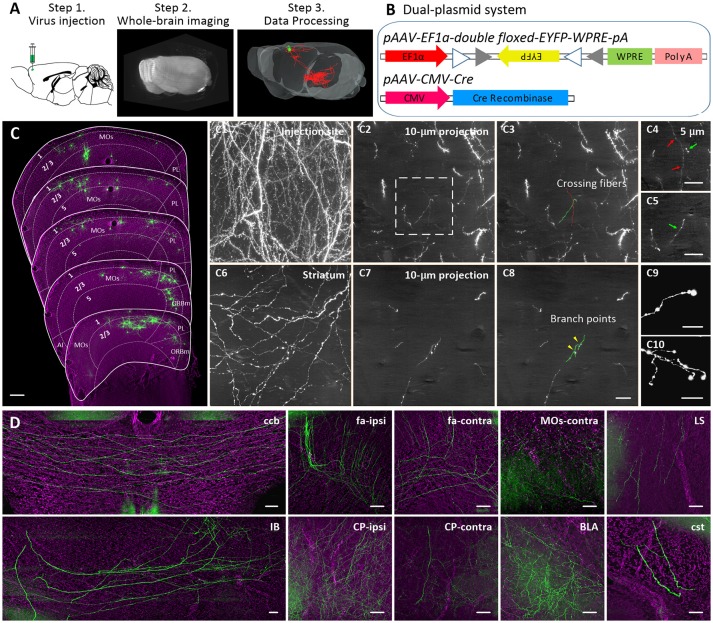
Figure 1.
A 3D dataset of a whole mouse brain. (A) Schematic showing the experimental processes, including virus injection, whole-brain imaging, and data processing. (B) The schematic diagram illustrates the dual-plasmid system of the AAV virus. (C) Distributions of labeled neurons in the frontal area. 1, 2/3, and 5 depict cortical layers. The dashed lines indicate the boundary of two adjacent regions. The length of the z stack is 100 μm. Representative raw images of the region near the cell bodies (C1–C3) and in the striatum (C6–C8) and terminals of axons (C9,C10). Representative image of axonal segments at crossing fibers (C3) and branch points (C8). (C4,C5) Magnifications of the region indicated in (C2). The arrows in different colors indicate the fibers corresponding to the fibers in (C3). Images are maximum intensity projections through a depth of 100 μm (C), 200 μm (C1,C6), 10 μm (C1–C3, C7,C8), and 5 μm (C4,C5). (D) Representative PI-merged local maximum intensity projections of the coronal planes in a GFP-positive area. AI, Agranular insular area; ccb, corpus callosum, body; fa, corpus callosum, anterior forceps; CP, Caudoputamen; IB, Interbrain; LS, Lateral septal nucleus; BLA, Basolateral amygdalar nucleus; cst, corticospinal tract. Scale bar, 200 μm (C); 10 μm (C1–C10); 50 μm (D).