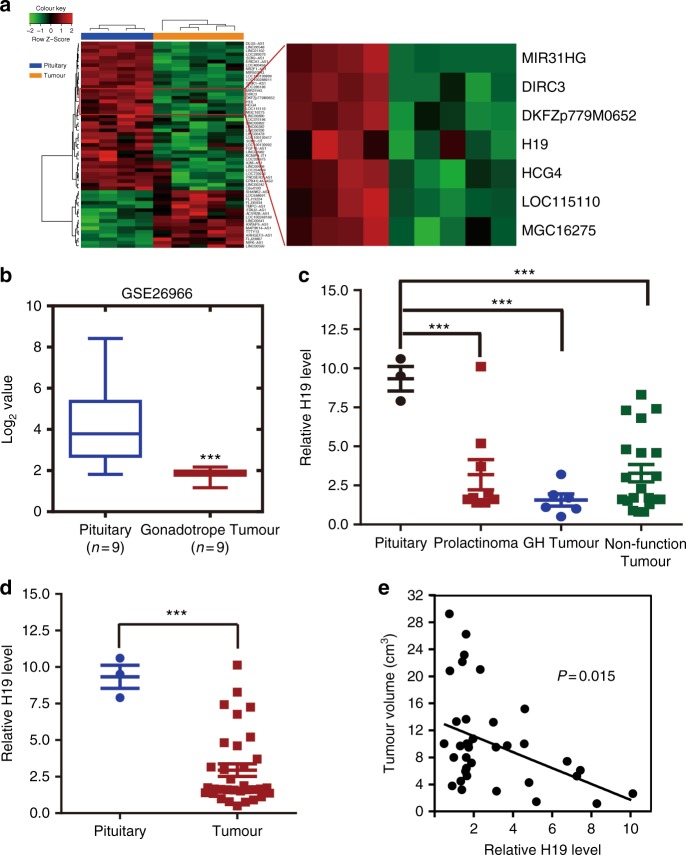
Fig. 1.
H19 expression is decreased in pituitary adenomas. a H19 expression is decreased in human prolactinomas compared with that in normal pituitary glands from healthy subjects. The SurePrint G3 Human GE 8 × 60 K Microarray was used to profile lncRNA expression in human normal pituitary glands and prolactinomas (GSE119063). Heatmap showing the differential expression of lncRNAs in normal pituitary (n = 4) and prolactinomas (n = 5), including the decreased level of H19 in prolactinomas. Right box plot panel shows that H19 expression is decreased approximately 1.51-fold in prolactinomas. b H19 expression is decreased in human gonadotropic adenoma (GEO dataset GSE26966). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. ***p < 0.001. c Decreased expression of H19 in prolactinomas, GH tumours and nonfunctioning pituitary tumours compared with that in three normal pituitary tissues. Statistical analysis was determined by paired Student’s t-test. ***p < 0.001. d H19 is decreased by 3.24-fold in 37 pituitary tumours compared with that in three normal pituitary tissues. Total RNA was extracted from 37 different subtypes of human pituitary tumours, and qRT-PCR was performed to assess H19 abundance in these pituitary adenomas (PRL = 9, NFPA = 20, GH = 6, ACTH = 2); mRNA levels were normalized to β-actin mRNA. ***p < 0.001, two-tailed Student’s t-test was used for statistical analysis. e H19 expression level is negatively corrected with tumour volume in patients (p = 0.015, by Pearson’s, n = 37). Error bars are the mean ± SEM values