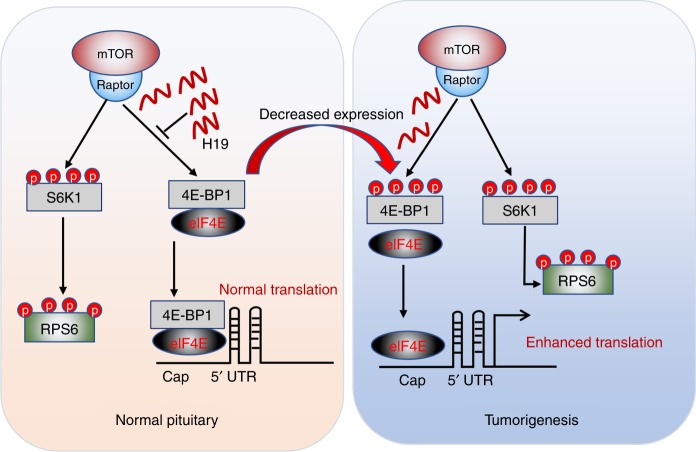
Fig. 8.
A model for H19-mediated regulation of 4E-BP1 phosphorylation. When H19 is abundant (right panel), mTORC1 activity is attenuated because H19 inhibits 4E-BP1 phosphorylation by disrupting the interaction between 4E-BP1 and Raptor. The reduced 4E-BP1 phosphorylation allows 4E-BP1 to bind elF4E, thus inhibiting its protein translation function. When H19 is absent, 4E-BP1 binds to Raptor and thus is more readily and effectively phosphorylated. This prevents its interaction with elF4E, resulting in increased protein translation