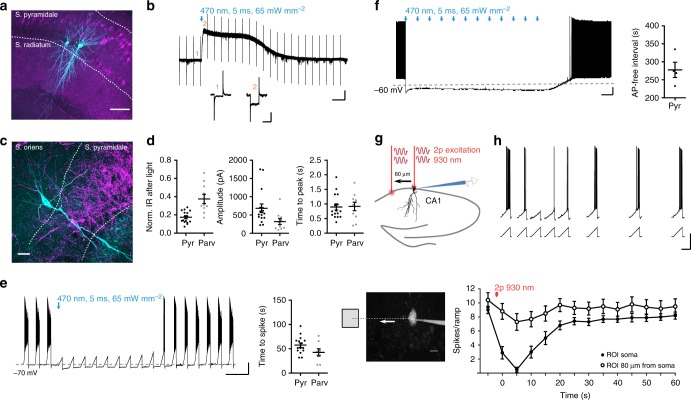
Fig. 5.
Silencing of neuronal activity in hippocampal slices. a Split-bPAC-K-mCherry-expressing pyramidal cells in area CA1. Recorded cells were filled with biocytin (green). Scale bar: 100 µm. b Blue light elicited outward current in a split-bPAC-K-positive pyramidal cell. Inset shows test pulse before (1) and after the light pulse (2). Scale bars: 10 s, 100 pA (overview trace); 50 ms, 100 pA (test pulses). c split-bPAC-K-mCherry expression in hippocampal slice of a parvalbumin-Cre transgenic mouse. Note the dense mCherry labeling in stratum pyramidale showing axons from parvalbumin-positive interneurons. Scale bar: 25 µm. d Quantification of the light-induced reduction in input resistance (IR), hyperpolarizing current amplitude, and time to peak after light pulse (pyramidal neurons: n = 16 from two mice; interneurons: n = 10 from three mice). e Suppression of current ramp-elicited APs by illumination. In pyramidal cells and parvalbumin-Cre+ interneurons, first spikes reappeared after 58 ± 5 and 43 ± 7 s, respectively (pyramidal neurons: n = 15 from two mice; interneurons: n = 8 from three mice). Scale bars: 10 s, 20 mV. f Repetitive illumination (every 20 s for 5 ms) caused long-lasting but reversible inhibition of constant current-elicited spiking (n = 4, one mouse). Scale bars: 20 s, 10 mV. g Two-photon activation of fused-bPAC-K in CA1 neurons. The two-photon laser was either positioned over the soma of a fused-bPAC-K-positive neuron, or shifted ~80 µm to an adjacent area. Scale bar: 10 µm. h Inhibition of firing by the two-photon beam pointing at the soma (closed circles) or shifted from the soma (open circles, n = 10, three mice). Data in panel a–f was obtained with split-bPAC-K, while data in panel g and h was obtained with fused-bPAC-K. Scale bars: 1 s, 25 mV. Error bars in all graphs represent SEM