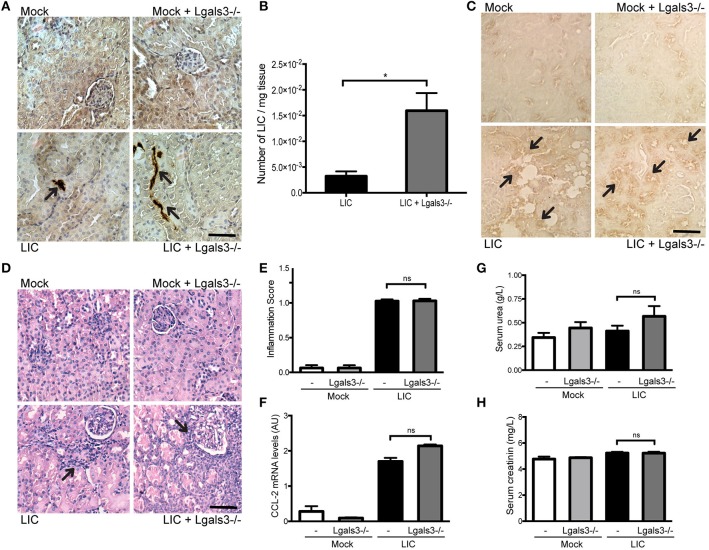
Figure 5.
Genetic disruption of Gal-3 significantly increased the chronic bacterial burden. (A) Immunostaining with an antibody against LipL32 (the major Leptospira interrogans antigen) in kidney sections of Mock, Mock + Lgals3−/−, LIC and LIC + Lgals3−/− groups of mice at 45 days post-infection (dpi). (B) Absence of galectin-3 in LIC-infected mice resulted in higher bacterial load in kidneys compared to wild-type LIC group. β-actin was used as a housekeeping control. (C) Immunostaining with an antibody against F4/80+ cells (macrophages) revealed its presence in both infected groups independent of galectin-3 absence. (D–F) Representative haematoxylin-eosin staining of kidney sections. An inflammation score was established by a pathologist and CCL-2 mRNA was quantified by qRT-PCR as a molecular marker of inflammation; β-actin was used as a housekeeping control. Similar chronic kidney inflammation was observed among experimental groups. (G,H) Normal urea and creatinine levels in serum samples from all experimental groups were detected and assayed as a measure of renal functions at 45 dpi. In all cases, data represent assays of two independent experiments of groups of 6 animals, each. Bars indicate 50 microns; AU, arbitrary units; nsP > 0.05; *P < 0.05.