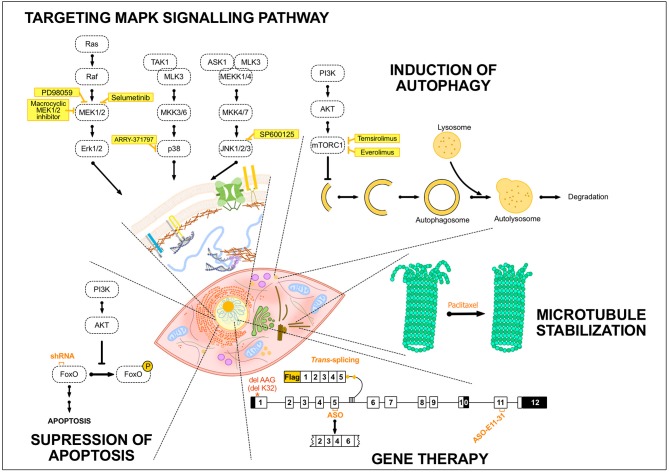
Figure 2.
Summary of the potential treatments tested so far in EDMD. Schematic drawing representing several treatment strategies that have been developed for EDMD. The portrayed treatments target diverse mechanisms occurring either in the cytoplasm, e.g., autophagy in the lysosomes, or in the nucleus, including exon-skipping or trans-splicing strategies. The treatment strategies addressed to EDMD have generally been developed to target MAPK signaling pathway or to induce autophagy and these include different inhibitors of components of these pathways such as selumetinib or temsirolimus. To target apoptosis, the utilization of shRNA specific to Fox O1 and 3 has been developed. Others treatments and strategies such as the use of paclitaxel to stabilize microtubules or gene therapy to convert the mutant transcript into a normal transcript or remove an in-frame exon containing a mutation have been studied. AKT, protein kinase B; ASK1, apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; ASO, antisense oligonucleotide; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FoxO, forkhead box O; MEK1/2, MAPK/ERK kinase 1/2; MEKK1/4, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1/4; MKK3/6, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3/6; MLK3, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 11; mTORC1, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; Raf, proto-oncogen serine/threonine-protein kinase; TAK1, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7.