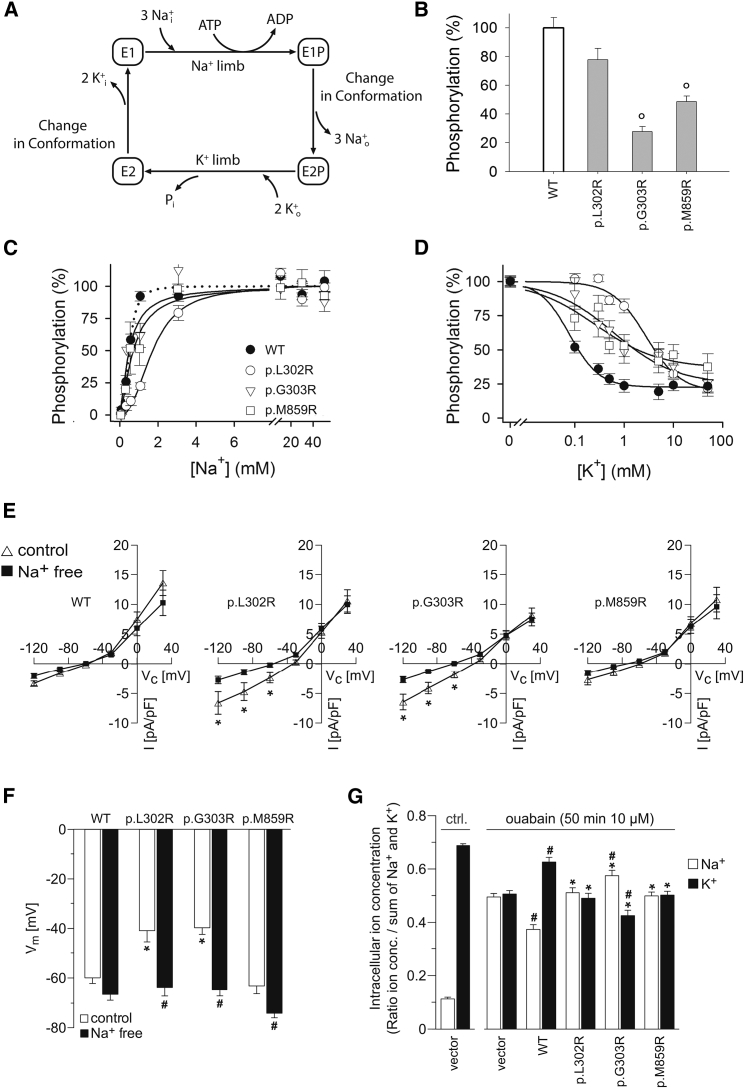
Figure 2.
Functional Characterization of Mutant ATP1A1 in Transfected Cells
Mutations corresponding to human ATP1A1 p.Leu302Arg (p.L302R), p.Gly303Arg (p.G303R), and p.Met859Arg (p.M859R) were introduced in rat α1 Na+, K+-ATPase (rat Atp1a1), which is insensitive to the inhibitor ouabain.
(A) Post-Albers scheme of the Na+, K+-ATPase reaction cycle.
(B) Transient expression of mutant enzymes with concomitant siRNA-mediated knockdown of endogenous Na+, K+-ATPase. All three mutants were phosphorylated with [γ-32P]-ATP in the Na+ reaction, indicating expression of mutant proteins and the ability to perform the Na+ limb of the Post-Albers reaction cycle (maximal phosphorylation signals relative to WT), albeit at a significantly reduced expression and/or phosphorylation level relative to that of WT, for p.Gly303Arg and p.Met859Arg (“o” = p < 0.001 for p.Gly303Arg and p.Met859Arg by a one-way ANOVA test; p = 0.027 for p.Leu302Arg; n = 3–5).
(C) Na+ dependence of phosphorylation showing a significant 3.5-fold reduced affinity for Na+ for p.Leu302Arg relative to WT, whereas the affinity was WT-like for p.Gly303Arg and p.Met859Arg, but with reduced cooperativity (see curves separated in different panels with statistics in Figure S1).
(D) K+-sensitivity of the Na+, K+-ATPase phosphoenzyme intermediate. Symbols are the same as in (C). K+ interaction was assessed by the ability of K+ to inhibit phosphorylation. The Hill equation for inhibition was used for data fitting.6 The cooperativity was WT-like for p.Leu302Arg (Hill coefficient 1.3–1.4), whereas the apparent affinity for K+ of this mutant was reduced significantly (p < 0.001 by a one-way ANOVA test, n = 8), 36-fold relative to WT. For p.Gly303Arg and p.Met859Arg, the Hill coefficients were only 0.6–0.7, indicating loss of cooperativity between the two K+ sites.
(E) Whole-cell currents of adrenal NCI-H295R cells expressing wild-type (WT) or different mutant (p.Leu302Arg, p.Gly303Arg, p.Met859Arg) ouabain-insensitive versions of rat Atp1a1. Compared to WT cells, mutant Atp1a1-expressing cells (except for mutant p.Met859Arg) displayed an abnormal current which was reduced after removal of Na+, indicating an abnormal Na+ permeability as causative for abnormal inward currents of Na+ ions in mutant cells.
(F) Mutant-expressing NCI-H295R cells (except for mutant p.Met859Arg) had a depolarized membrane potential under control conditions but were hyperpolarized to the level of WT cells after removal of extracellular Na+.
(G) Intracellular Na+ and K+ contents in cell lysates of HEK293 cells under control conditions and after treatment with the Na+, K+-ATPase inhibitor ouabain. Ouabain treatment strongly increased intracellular Na+ and decreased intracellular K+ in non-transfected cells. Expression of WT rat Atp1a1 significantly attenuated these changes of intracellular Na+ and K+, whereas this was not the case for all mutant-expressing cells. Expression of the p.Gly303Arg mutant increased Na+ and decreased K+ even more in comparison to vector control cells. n = 7–9 per group.
(B–G) (all data are presented as means ± SEM).