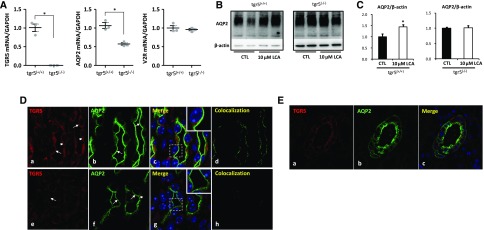
Figure 6.
TGR5 gene-deficient mice exhibited reduced renal AQP2 mRNA and protein expression. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis showed a complete suppression of TGR5 mRNA with a decreased mRNA level of AQP2 and unchanged mRNA level of V2R in the inner medulla of tgr5−/− mice compared with tgr5+/+ mice (A); n=3 biologically independent samples in each group. Data are presented as mean±SEM; *P<0.05 versus tgr5+/+ mice. LCA failed to increase AQP2 protein expression in IMCD cells prepared from tgr5−/− mice (B and C); n=4 biologically independent samples in each group. Data are presented as mean±SEM; *P<0.05 versus control. Immunofluorescence showed codistribution of TGR5 (red) and AQP2 (green) in principal cells of IMCDs of tgr5+/+ mouse kidney (D) (a–d). TGR5 labeling of tgr5−/− mice was markedly diminished, although the background fluorescence was retained (D) (e–h). Arrows: apical membrane, arrowheads: intracellular compartments. Magnification 10×63; Original magnification: ×2 (insets). TGR5 and AQP2 were expressed in the cortical collecting ducts in human kidneys (E). Magnification 20×63. CTL, control.