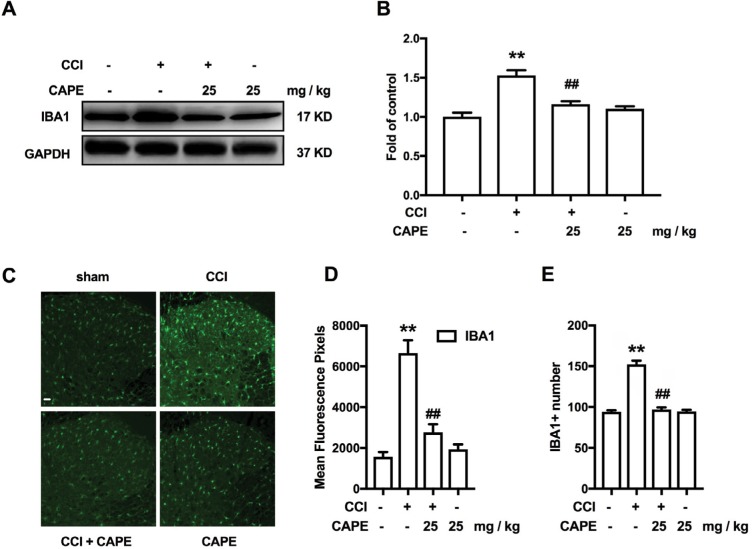
Figure 2.
CAPE significantly inhibited CCI-induced activation of microglia.
Notes: (A, B) Effects of CAPE (25 mg/kg, i.p.) on the expression of IBA-1 in the spinal cord. (C-E) Confocal images and immunofluorescence analysis data showing IBA-1 in the dorsal horns. Quantification of immunofluorescence was represented as the mean fluorescence pixels in the superficial dorsal horns. CAPE was consecutively administered daily from day 15 to day 21 after CCI operation. The lumbar spines (L1–L6) were collected and analyzed 60 minutes after the last drug administration. n=4. Two-way ANOVA revealed a significant difference at **P<0.01 vs sham; and ##P<0.01 vs CCI. Scale bar 50μm, original magnification ×200.
Abbreviations: CAPE, caffeic acid phenethyl ester; CCI, chronic constrictive injury; IBA-1, ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1; i.p., intraperitoneal.