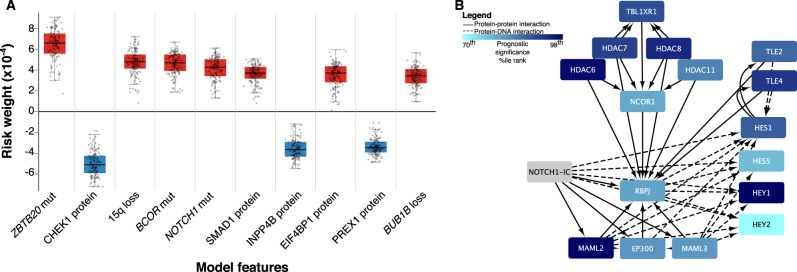
Fig. 1.
a Neural network risk factors. A nonlinear Cox proportional hazards model was trained using a neural network to model survival in oligodendrogliomas using clinical, genetic and proteomic factors. Prognostic significance of each feature was assessed by determining how its changes impact prognosis. Positive scores indicate a negative impact on survival (red) while negative scores (blue) suggest a positive impact. The boxplot contains the top 10 factors ranked by median prognostic importance; complete results in Datafile S1. b Gene set enrichment analysis of Notch pathway members. A separate model based on mRNA expression weighed the prognostic significance of individual transcripts and used this data in a gene-set-enrichment analysis to identify pathways associated with prognosis. The canonical Notch pathway was highly enriched with significantly negatively scored transcripts (i.e., darker blue signifies negative scores). Increased expression of downstream targets, including HES1, HES5, and HEY1, were associated with improved prognosis. This model demonstrates Notch signaling inactivation is associated with poor prognosis