Figure 4.
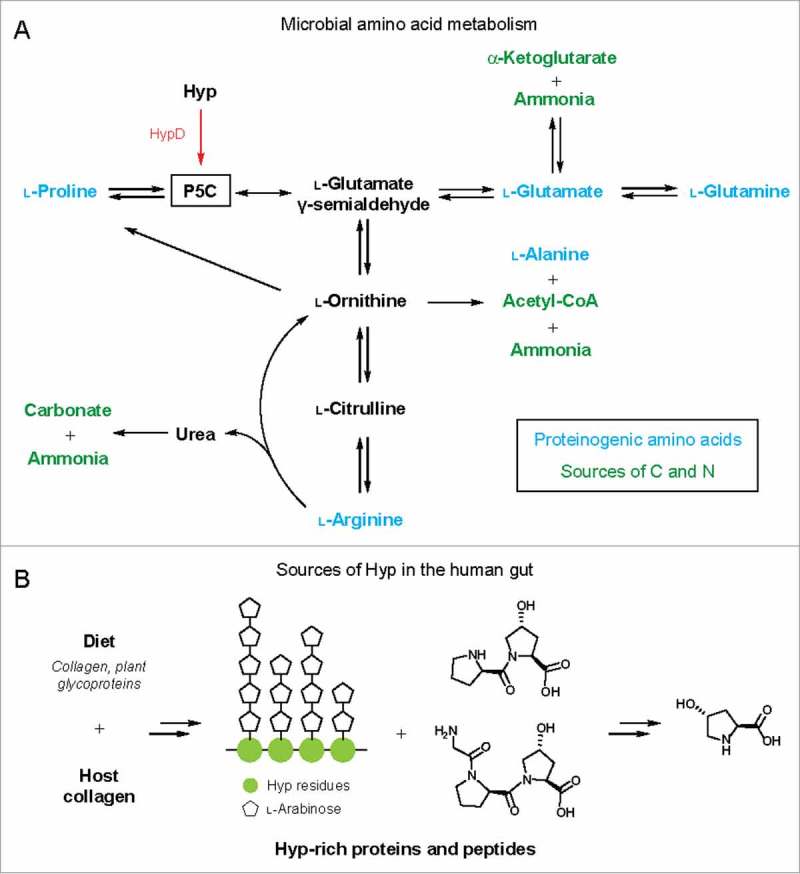
(A) Hyp metabolism by HypD interfaces with microbial amino acid metabolic pathways. Arrows can represent multiple steps and only key metabolites are shown. P5C is a central intermediate in amino acid metabolism. The downstream metabolites α-KG, carbonate, acetyl-CoA, and ammonia can serve as sources of carbon and nitrogen. (B) Sources of Hyp in the human gut from diet or endogenous collagen turnover. Major collagen-derived peptides and Hyp repeats from extensin, a plant cell wall glycoprotein, are shown as examples.
