Figure 1.
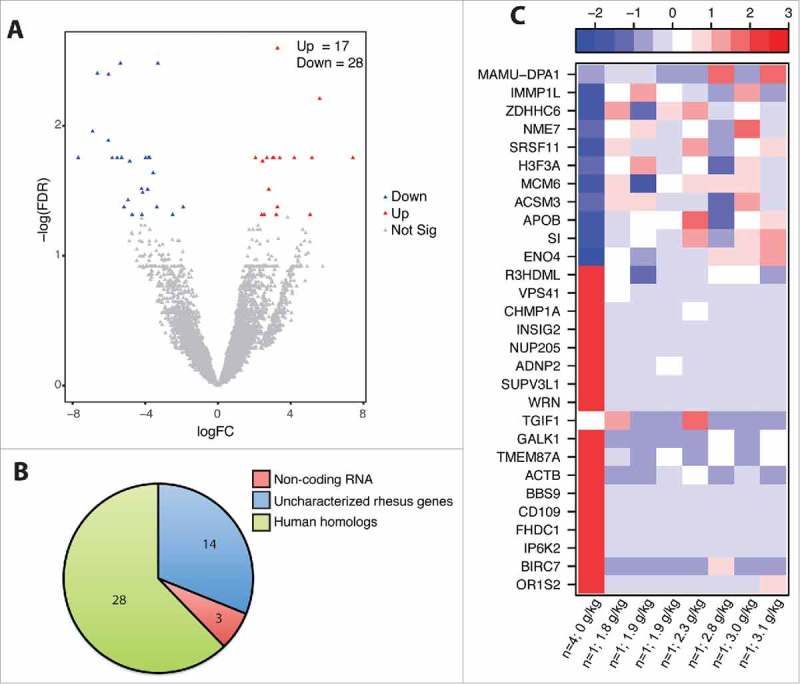
Chronic ethanol consumption modulates jejunum mucosal gene expression. DEG were identified using the generalized linear model likelihood ratio test method from the edgeR package as those with a fold change of ≥2 and a Benjamini-Hochberg- corrected false discovery rate (FDR) of <0.05. (A) Volcano plot summarizing the gene expression changes with red representing the upregulated DEG and blue representing the downregulated DEG. The number of up- and down-regulated genes is noted. (B) Pie chart representing the breakdown of DEG as: noncoding RNA, uncharacterized rhesus genes, and human homologs. (C) Heatmap representing gene expression (shown as absolute normalized RPKM values) of the genes listed; first column shows median RPKM values of the controls (n = 4), and subsequent columns show RPKM values of each individual ethanol-consuming animals ordered by alcohol dose (g of ethanol/kg/day); range of colors is based on scaled and centered RPKM values of the entire set of genes (red represents increased expression while blue represents decreased expression).
