Figure 6.
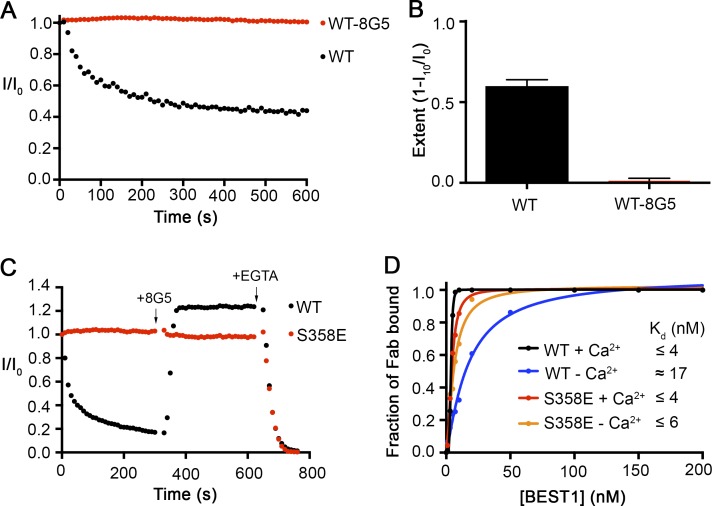
The 8G5 Fab prevents inactivation of BEST1WT. (A) The Ca2+-dependent inactivation of BEST1WT and BEST1WT–8G5 complex. Recordings were done as described in Fig. 1 A, using 50 µM Ca2+. For the experiment with the 8G5 Fab, after currents for BEST1WT were obtained, 8G5 Fab was added (300 nM final concentration) to the cis and trans chambers, and the chambers were stirred for 2 min before the start of the recording. 50 μM CaCl2 was added at the start (time = 0) of each recording. (B) Extent of inactivation in 50 µM Ca2+ after 10 min is plotted for BEST1WT and the BEST1WT–8G5 complex. Data are derived from A, and at least three separate experiments were performed to calculate SE. (C) Rescue of inactivated BEST1WT channels by 8G5. From time = 0, currents from BEST1WT and BEST1S358E were recorded using 100 µM Ca2+ conditions. At the 5-min mark, 300 nM 8G5 Fab was added to both sides of the bilayer. At the 10-min mark, 10 mM EGTA (final concentration) was added to both sides of the bilayer to chelate free Ca2+. Solutions were stirred for the duration of the experiment. (D) The relative binding of 8G5 Fab to BEST1WT and BEST1S358E was assayed by determining the amount of free 8G5 as a function of the concentration of BEST1 in conditions containing either 10 µM Ca2+ (+Ca2+) or 5 mM EGTA (−Ca2+; Materials and methods). The curves correspond to fits of the following: fraction of Fab bound = [BEST1]h/(Kdh + [BEST1]h), where Kd is the equilibrium dissociation constant, h is the Hill coefficient, and [BEST1] is the total concentration of BEST1. Derived Kd values are indicated.