Figure 5.
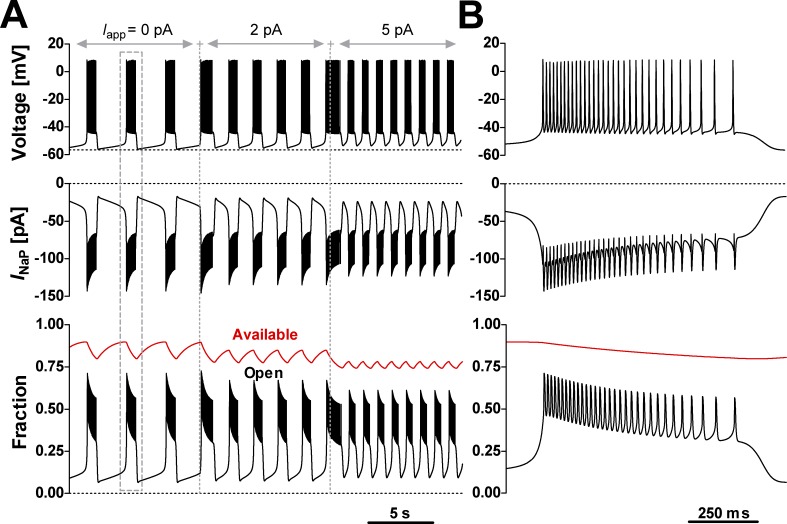
INaP Model 1 supports voltage-dependent rhythmic bursting in computer simulations. The INaP model was tested in a single-compartment neuronal model that also includes spike-generating and -terminating Na+ and K+ currents, and a K+-dominated leak (see Materials and methods for details). A bias current (Iapp) was applied to test bursting activity at different baseline voltages. (A) Time course of membrane potential (upper trace), INaP (middle trace), and the fractions of INaP channels residing in the open state (bottom graph, black trace) and available to conduct current (bottom graph, red trace). Availability was calculated as the sum occupancy of all states other than SI11 and SI12. (B) Expanded view of a single burst (dashed box in A). The simulations exhibit the bAHP, the depolarization drift in the interburst interval, and the voltage-dependent bursting frequency characteristic of preBötC intrinsic burster neurons (Fig. 1 D).